| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name Bromine pentafluoride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.234 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1745 | ||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | BrF5 | ||
| Molar mass | 174.894 g.mol | ||
| Appearance | Pale yellow liquid | ||
| Density | 2.466 g/cm | ||
| Melting point | −61.30 °C (−78.34 °F; 211.85 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 40.25 °C (104.45 °F; 313.40 K) | ||
| Solubility in water | Reacts with water | ||
| Structure | |||
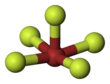
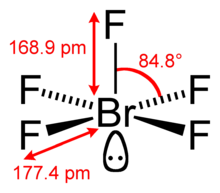
| Molecular shape | Square pyramidal | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
| Main hazards | Powerful oxidizer, corrosive, highly toxic, reacts violently with water to release HF | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| Pictograms |    
| ||
| Signal word | Danger | ||
| Hazard statements | H271, H300+H310+H330, H314, H372 | ||
| Precautionary statements | P210, P220, P221, P260, P264, P270, P271, P280, P283, P284, P301+P310, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P306+P360, P307+P311, P309+P311, P310, P314, P320, P321, P331, P363, P370+P378, P371+P380+P375, P403+P233, P405, P501 | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 OX | ||
| Flash point | Non-flammable | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
| PEL (Permissible) | none | ||
| REL (Recommended) | TWA 0.1 ppm (0.7 mg/m) | ||
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | N.D. | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Other anions | Bromine monochloride | ||
| Other cations | Chlorine pentafluoride Iodine pentafluoride | ||
| Related compounds | Bromine monofluoride Bromine trifluoride | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Bromine pentafluoride (data page) | |||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
Bromine pentafluoride, BrF5, is an interhalogen compound and a fluoride of bromine. It is a strong fluorinating agent.
BrF5 finds use in oxygen isotope analysis. Laser ablation of solid silicates in the presence of BrF5 releases O2 for subsequent analysis. It has also been tested as an oxidizer in liquid rocket propellants and is used as a fluorinating agent in the processing of uranium.
Preparation
BrF5 was first prepared in 1931 by the direct reaction of bromine and fluorine. This reaction is suitable for the preparation of large quantities, and is carried out at temperatures over 150 °C (302 °F) with an excess of fluorine:
- Br2 + 5 F2 → 2 BrF5
For the preparation of smaller amounts, potassium bromide is used:
- KBr + 3 F2 → KF + BrF5
This route yields BrF5 almost completely free of trifluorides and other impurities.
Reactions
BrF5 reacts with water to form bromic acid and hydrofluoric acid:
- BrF5 + 3 H2O → HBrO3 + 5 HF
It is an extremely effective fluorinating agent, being able to convert most metals to their highest fluorides even at room temperature. With uranium and uranium compounds, it can be used to produce uranium hexafluoride:
- 5 U + 6 BrF5 → 5 UF6 + 3 Br2
Hazards
BrF5 reacts violently with water, and is severely corrosive and toxic. Its vapors are also extremely irritating to all parts of the human body, especially the skin, eyes and other mucous membranes. Like many other interhalogen compounds, it will release "smoke" containing acidic vapors if exposed to moist air, which comes from its reaction with the water in the air. Exposure to 100 ppm or more for more than one minute is lethal to most experimental animals. Chronic exposure may cause kidney damage and liver failure.
Additionally, BrF5 is a strong oxidizing agent and may spontaneously ignite or explode upon contact with flammable substances such as organic materials and metal dust.
References
- ^ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0065". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Clayton, R.; Mayeda, T. K. (1963). "The use of bromine pentafluoride in the extraction of oxygen from oxides and silicates for isotopic analysis". Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 27 (1): 43–48. Bibcode:1963GeCoA..27...43C. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(63)90071-1.
- ^ Hyde, G. A.; Boudakian, M. M. (1968). "Synthesis routes to chlorine and bromine pentafluorides". Inorganic Chemistry. 7 (12): 2648–2649. doi:10.1021/ic50070a039.
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 834. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Patnaik, Pradyot (2007). A comprehensive guide to the hazardous properties of chemical substances (3rd ed.). Wiley-Interscience. p. 480. ISBN 978-0-471-71458-3.
External links
- WebBook page for BrF5
- International Chemical Safety Card 0974
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0065". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- National Pollutant Inventory - Fluoride and compounds fact sheet
| Bromine compounds | |
|---|---|
| Br(−I) | |
| Br(−I,I) | |
| Br(I) | |
| Br(II) | |
| Br(I,V) | |
| Br(III) | |
| Br(IV) | |
| Br(V) | |
| Br(VII) | |