 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
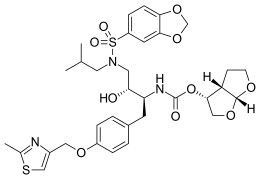
| Formula | C33H41N3O10S2 |
| Molar mass | 703.82 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Brecanavir (INN; codenamed GW640385) is a protease inhibitor which has been studied for the treatment of HIV.
In December 2006, its developer, GlaxoSmithKline discontinued further development because of insurmountable issues regarding formulation.
See also
References
- Hazen R, Harvey R, Ferris R, et al. (September 2007). "In vitro antiviral activity of the novel, tyrosyl-based human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 protease inhibitor brecanavir (GW640385) in combination with other antiretrovirals and against a panel of protease inhibitor-resistant HIV". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 (9): 3147–54. doi:10.1128/AAC.00401-07. PMC 2043237. PMID 17620375.
- "GlaxoSmithKline discontinues clinical development of investigational protease inhibitor brecanavir (640385)" (Press release). GlaxoSmithKline. 2006-12-18. Archived from the original on 2008-12-03. Retrieved 2008-06-11.
This antiinfective drug article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |