| This article needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (January 2014) |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
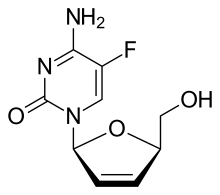
| Formula | C9H10FN3O3 |
| Molar mass | 227.195 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Elvucitabine is an experimental nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI), developed by Achillion Pharmaceuticals, Inc. for the treatment of HIV infection.
Elvucitabine belongs to a class of HIV drugs called nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs). By blocking reverse transcriptase enzymes, NRTIs prevent HIV from multiplying and can reduce the amount of HIV in the body.
Elvucitabine is similar in chemical structure to the FDA-approved NRTIs lamivudine (brand name Epivir) and emtricitabine (brand name Emtriva). However, in vitro studies have suggested that elvucitabine may affect certain HIV strains resistant to other NRTIs, such as lamivudine and emtricitabine.
Studies have also suggested that elvucitabine may be effective against hepatitis B virus (HBV). Mechanism of action of Elvucitabine ; reveals that it acts by inhibiting reverse transcriptase which interferes with generation of DNA copies of viral RNA.
Currently, it is in Phase II clinical trials.
References
- Ghosh RK, Ghosh SM, Chawla S (January 2011). "Recent advances in antiretroviral drugs". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 12 (1): 31–46. doi:10.1517/14656566.2010.509345. PMID 20698725. S2CID 20414056.
- "HIV Drugs in Development". National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID). United States National Institutes of Health. Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 2014-11-22.
- Block TM, Rawat S, Brosgart CL (September 2015). "Chronic hepatitis B: A wave of new therapies on the horizon". Antiviral Research. 121: 69–81. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.06.014. PMC 5391532. PMID 26112647.
- "Elvucitabine".
- "Elvucitabine". AIDSmeds.com. November 5, 2007. Archived from the original on March 21, 2008. Retrieved March 21, 2008.
This antiinfective drug article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |