| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
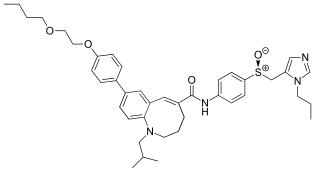
| Preferred IUPAC name (5E)-8--1-(2-methylpropyl)-N-{4-phenyl}-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-benzazocine-5-carboxamide | |
| Other names TAK-652; TBR-652 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C41H52N4O4S |
| Molar mass | 696.95 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Cenicriviroc (INN, code names TAK-652, TBR-652, commonly abbreviated as CVC) is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of HIV infection and in combination with Tropifexor for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. It is being developed by Takeda and Tobira Therapeutics.
Cenicriviroc is an inhibitor of CCR2 and CCR5 receptors, allowing it to function as an entry inhibitor which prevents the virus from entering into a human cell. Inhibition of CCR2 may have an anti-inflammatory effect.
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical study to assess the antiviral activity, safety, and tolerability of cenicriviroc was conducted in 2010. HIV-infected patients taking cenicriviroc had significant reductions in viral load, with the effect persisting up to two weeks after discontinuation of treatment. Additional Phase II clinical trials are underway.
Cenicriviroc is also in two separate clinical trials for COVID-19: the ACTIV-I trial run by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, where it is compared with a number of other immunomodulatory agents, and the Charité Trial of Cenicriviroc at the Charité Hospital in Berlin. As of 2 July 2021, both trials are recruiting participants, and are expected to complete in September 2021.
Phase IIb data presented at the 20th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) in March 2013 showed similar viral suppression rates of 76% for patients taking 100 mg cenicriviroc, 73% with 200 mg cenicriviroc, and 71% with efavirenz. Non-response rates were higher with cenicriviroc, however, largely due to greater drop-out of patients. A new tablet formulation with lower pill burden may improve adherence. Looking at immune and inflammatory biomarkers, levels of MCP-1 increased and soluble CD14 decreased in the cenicriviroc arms.
See also
References
- "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names: List 65" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2011. pp. 53–4. Retrieved 25 November 2016.
- Klibanov, OM; Williams, SH; Iler, CA (August 2010). "Cenicriviroc, an Orally Active CCR5 Antagonist for the Potential Treatment of HIV Infection". Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs. 11 (8): 940–50. PMID 20721836.
- "A Randomized, Double-blind, Multicenter Study to Assess the Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy of a Combination Treatment of Tropifexor (LJN452) and Cenicriviroc (CVC) in Adult Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) and Liver Fibrosis". 21 January 2022.
- Baba, M; Takashima, K; Miyake, H; Kanzaki, N; Teshima, K; Wang, X; Shiraishi, M; Iizawa, Y (26 October 2005). "TAK-652 Inhibits CCR5-Mediated Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection In Vitro and Has Favorable Pharmacokinetics in Humans". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 49 (11): 4584–91. doi:10.1128/AAC.49.11.4584-4591.2005. PMC 1280155. PMID 16251299.
- Reviriego, C (July 2011). "Chemokine CCR2/CCR5 Receptor Antagonist Anti-HIV Agent". Drugs of the Future. 36 (7): 511–7. doi:10.1358/dof.2011.036.07.1622066.
- "Tobira Therapeutics Initiates Phase 2b Trial of Cenicriviroc". The Body. July 5, 2011.
- Benjamin, Daniel (2021-06-29). "Randomized Master Protocol for Immune Modulators for Treating COVID-19". Daniel Benjamin, National Center for Advancing Translational Science (NCATS), Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority.
- Tacke, Frank (2020-08-25). "Charité Trial of Cenicriviroc (CVC) Treatment for COVID-19 Patients". Charite University, Berlin, Germany, Allergan.
- CROI 2013: CCR5/CCR2 Inhibitor Cenicriviroc Has Both Anti-HIV and Anti-inflammatory Effects. Highleyman, Liz. HIVandHepatitis.com. 7 March 2013.
| Chemokine receptor modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CXC |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C (XC) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CX3C |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||