 | |
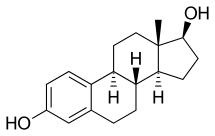
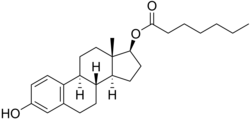 Estradiol (top) and Estradiol (top) andestradiol enanthate (bottom) | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Estradiol | Estrogen |
| Estradiol enanthate | Estrogen |
| Clinical data | |
| Other names | E2/E2-EN; E2/EEn |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular injection |
Estradiol/estradiol enanthate (E2/E2-EN) is an injectable combination formulation of estradiol (E2), a short-acting estrogen, and estradiol enanthate (E2-EN), a long-acting estrogen, which was developed by Boehringer around 1960 for potential medical use but was never marketed. It contained 1 mg E2 and 9 mg E2-EN in oil solution and was intended for administration by intramuscular injection.
A single intramuscular injection of E2/E2-EN (1 mg/9 mg) has been found to result in a 10-fold increase in estradiol excretion on the 2nd day post-injection (due to the 1 mg short-acting E2 component). Following this, estradiol excretion remained above the menstrual-cycle average for 10 days post-injection and did not return to baseline until the 24th day post-injection (due to the 9 mg long-acting E2-EN component).
E2/E2-EN is similar to estradiol benzoate/estradiol phenylpropionate (brand name Dimenformon Prolongatum), another injectable combination medication of a shorter-acting estrogen (2.5 mg) and a longer-acting estrogen (10 mg). In contrast to E2/E2-EN however, estradiol benzoate/estradiol phenylpropionate was marketed for medical use.
See also
- Estradiol benzoate/estradiol phenylpropionate
- Estradiol benzoate/estradiol valerate/hydroxyprogesterone caproate
- List of combined sex-hormonal preparations
References
- ^ Kaiser R (September 1961). "Die Östrogenausscheidung im Zyklus und nach Injektion von Östradiolestern. Ein Beitrag zur Therapie mit Depotöstrogenen" [Estrogen excretion during the cycle and after injection of estradiol esters. A contribution to therapy with depot estrogens]. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd (in German). 21: 868–78. ISSN 0016-5751. PMID 13750804.
- ^ Kaiser, R (1962). "Über die Oestrogenausscheidung nach Injektion von Oestradiolestern" [Estrogen excretion after injection of estradiol esters]. Gewebs-und Neurohormone: Physiologie des Melanophorenhormons [Tissue and Neurohormones: Physiology of the Melanophore Hormone] (in German). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. pp. 227–232. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-86860-3_24. ISBN 978-3-540-02909-0.
| Estrogen receptor modulators | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERTooltip Estrogen receptor |
| ||||||
| GPERTooltip G protein-coupled estrogen receptor |
| ||||||
This drug article relating to the genito-urinary system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |