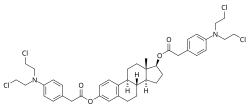
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | NSC-112259; Estradiol 3,17β-bis(4-(bis(2-chloroethyl)amino)phenyl)acetate |
| Drug class | Chemotherapeutic agent; Estrogen; Estrogen ester |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C42H50Cl4N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 788.67 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Estradiol mustard, also known as estradiol 3,17β-bis(4-(bis(2-chloroethyl)amino)phenyl)acetate, is a semisynthetic, steroidal estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent and a phenylacetic acid nitrogen mustard-coupled estrogen ester that was never marketed. It is selectively distributed into estrogen receptor (ER)-positive tissues such as ER-expressing tumors like those seen in breast and prostate cancers. For this reason, estradiol mustard and other cytostatic-linked estrogens like estramustine phosphate have reduced toxicity relative to non-linked nitrogen mustard cytostatic antineoplastic agents. However, they may stimulate breast tumor growth due to their inherent estrogenic activity and are said to be devoid of major therapeutic efficacy in breast cancer, although estramustine phosphate has been approved for and is used (almost exclusively) in the treatment of prostate cancer.
See also
References
- Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 898–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ^ Asai M, Takeuchi H, Okada H (January 1978). "In vivo interaction between steroidal alkylating agents and oestrogen receptors in rabbit uteri". Acta Endocrinologica. 87 (1): 173–180. doi:10.1530/acta.0.0870173. PMID 579532.
- Leclercq G, Devleeschouwer N, Heuson JC (July 1983). James VH, Pasqualini JR (eds.). "Guide-lines in the design of new antiestrogens and cytotoxic-linked estrogens for the treatment of breast cancer". Journal of Steroid Biochemistry. 19 (1A). Elsevier Science: 75–85. doi:10.1016/S0022-4731(83)80009-0. ISBN 978-1-4831-9067-9. PMID 6887875.
- Scullin P, O'Sullivan JM, Parker CC (5 September 2007). "Strategies for the Implementation of Chemotherapy". In Ablin RJ, Mason MD (eds.). Metastasis of Prostate Cancer. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 311–. ISBN 978-1-4020-5847-9.
This article about a steroid is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This drug article relating to the genito-urinary system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This antineoplastic or immunomodulatory drug article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |