| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Flufenoxuron" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
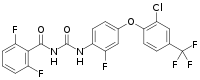
| Preferred IUPAC name N-({4--2-fluorophenyl}carbamoyl)-2,6-difluorobenzamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.101.654 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C21H11ClF6N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 488.77 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Flufenoxuron is an insecticide that belongs to the benzoylurea chitin synthesis inhibitor group, which also includes diflubenzuron, triflumuron, and lufenuron.
Flufenoxuron is a white crystalline powder. It is insoluble in water, is not flammable, and is not an oxidizer.
Toxicology and safety
Flufenoxuron toxicity to humans and other mammals is low, but it has a very high bioaccumulation in fish.
References
- "Flufenoxuron". NIH - National Center for Biotechnology Information.
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |