| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.032.021 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | RhO2 |
| Molar mass | 134.904 g/mol |
| Appearance | black crystalline solid |
| Density | 7.2 g/cm |
| Melting point | 1,050 °C (1,920 °F; 1,320 K) (decomposes) |
| Solubility | insoluble in aqua regia |
| Structure | |
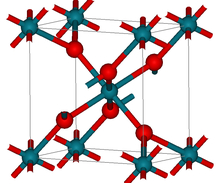
| Crystal structure | tetragonal (rutile) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Rhodium(IV) oxide (or rhodium dioxide) is the chemical compound with the formula RhO2.
Chemical properties
RhO2 is highly insoluble even in hot aqua regia.
Structure
RhO2 has the tetragonal rutile structure.
Physical properties
RhO2 has metallic resistivity with values <10 Ohm·cm. It transforms in air to Rh2O3 at 850 °C and then to metal and oxygen at 1050 °C.
See also
References
- O. Muller and R. Roy (1968). "Formation and stability of the platinum and rhodium oxides at high oxygen pressures and the structures of Pt3O4, β-PtO2 and RhO2". Journal of the Less Common Metals. 16 (2): 129–146. doi:10.1016/0022-5088(68)90070-2.
- ^ R. D. Shannon (1968). "Synthesis and properties of two new members of the rutile family RhO2 and PtO2". Solid State Communications. 6 (3): 139–143. Bibcode:1968SSCom...6..139S. doi:10.1016/0038-1098(68)90019-7.
| Rhodium compounds | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rh(0) |
| ||
| Rh(I) |
| ||
| Rh(II) |
| ||
| Rh(III) |
| ||
| Rh(IV) | |||
| Rh(V) | |||
| Rh(VI) | |||
This inorganic compound–related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |