
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C12H28BF4O18Ru3 |
| Molar mass | 850.35 g·mol |
| Appearance | green solid |
| Density | 2.110 g/cm |
| Structure | |
| Coordination geometry | octahedral |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H318, H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P273, P280, P305+P351+P338, P310, P391, P501 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | Manganese(III) acetate Iron(III) acetate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Ruthenium(III) acetate, commonly known as basic ruthenium acetate, describes a family of salts where the cation has the formula . A representative derivative is the dihydrate of the tetrafluoroborate salt BF4(H2O)2, which is the source of the data in the table above. This and related salts are forest green, air-stable solids that are soluble in alcohols.
Basic ruthenium acetate features octahedral Ru(III) centers, a triply bridging oxo ligand, six acetate ligands, and three aquo ligands. The same structure is shared with basic acetates of iron, chromium, iridium, and manganese.
Preparation and reactions
It is prepared by heating ruthenium trichloride in acetic acid in the presence of sodium acetate. The basic acetates of ruthenium were reported in the early 1950s but were not properly formulated.
Basic ruthenium acetate reacts with many ligands such as triphenylphosphine and pyridine concomitant with reduction. These derivatives are mixed valence compounds.
Related compounds
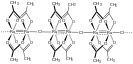
n is a coordination polymer with a composition similar to that of ruthenium(III) acetate.
References
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ O. Almog; A. Bino; D. Garfinkel-Shweky (1993). "The Structure of Oxo-Bridged Trinuclear Ruthenium and Iridium Hexacarboxylates". Inorg. Chim. Acta. 213 (1–2): 99. doi:10.1016/S0020-1693(00)83819-0.
- J. C. Goeltz; S. D. Glover; J. Hauk; C. P. Kubiak (2010). "Ruthenium Complexes". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 35. pp. 156–160. doi:10.1002/9780470651568.ch8. ISBN 978-0-470-65156-8.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - Martin, F. S. (1952). "Basic Trinuclear Ruthenium Acetate". Journal of the Chemical Society: 2682–4. doi:10.1039/jr9520002682.
- Cotton, F. A.; Norman, J. G. Jr. (1972). "Structural Characterization of a Basic trinuclear Ruthenium Acetate". Inorg. Chim. Acta. 6: 411–419. doi:10.1016/S0020-1693(00)91829-2.
| Ruthenium compounds | |
|---|---|
| Ru(0) | |
| Ru(I) | |
| Ru(II) | |
| Ru(II,III) | |
| Ru(III) |
|
| Ru(IV) | |
| Ru(V) | |
| Ru(VI) | |
| Ru(VII) | |
| Ru(VIII) | |
| Acetyl halides and salts of the acetate ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||