
| |
 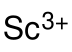
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Scandium(III) acetate Scandium ethanoate Scandium(III) ethanoate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.021.159 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H9O6Sc |
| Molar mass | 222.088 g·mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Scandium acetate is a compound, with the chemical formula of Sc(CH3COO)3. It exists in the anhydrous and the hydrate forms. It can be obtained by reacting scandium hydroxide or scandium oxide with acetic acid. It is a colorless, water-soluble solid. It decomposes into scandium oxide at high temperature. It can be used to prepare other scandium-containing materials.
The structure of the anhydrous form was determined by X-ray crystallography. It consists of a chain of octahedral Sc(III) centers linked by bridging acetate ligands.
References
- ^ Fuchs, Robert; Strähle, Joachim (1984). "Die Kristallstruktur von Sc(CH3COO)3, ein Metall(III)acetat mit Kettenstruktur" [Crystal Structure of Sc(CH3COO)3, a Metal(III) Acetate with a Chain Structure]. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B. 39 (12): 1662–1663. doi:10.1515/znb-1984-1206.
- Krasil'Nikov, V. N.; Gyrdasova, O. I.; Baklanova, I. V.; Perelyaeva, L. A.; Zhilina, E. F.; Vovkotrub, É. G. (2012). "Structure and luminescence properties of nanostructured solid-state solutions of Sc1−xEux(CH3CO2)3". Theoretical and Experimental Chemistry. 48 (2): 113–117. doi:10.1007/s11237-012-9247-9.
- Xin, Chengrong; Zhang, Qilong; Yang, Hui (2013). "Synthesis and Properties Study of BaTi0.95Sc0.05O3−δ Nanopowders and Ceramics". Piezoelectrics & Acoustooptics (in Chinese). 35 (3): 412–415.
| Scandium compounds | |
|---|---|
| Acetyl halides and salts of the acetate ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||