 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| Routes of administration | Injection |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.067.337 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
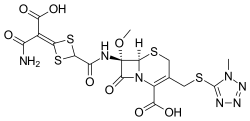
| Formula | C17H17N7O8S4 |
| Molar mass | 575.60 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Cefotetan is an injectable antibiotic of the cephamycin type for prophylaxis and treatment of bacterial infections. It is often grouped together with second-generation cephalosporins and has a similar antibacterial spectrum, but with additional anti-anaerobe coverage.
Cefotetan was developed by Yamanouchi. It is marketed outside Japan by AstraZeneca with the brand names Apatef and Cefotan.
Adverse effects
The chemical structure of cefotetan, like that of several other cephalosporins, contains an N-methylthiotetrazole (NMTT or 1-MTT) side chain. As the antibiotic is broken down in the body, it releases free NMTT, which can cause hypoprothrombinemia (likely due to inhibition of the enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase) and a reaction with ethanol similar to that produced by disulfiram (Antabuse), due to inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase.
Spectrum of bacterial susceptibility
Cefotetan has a broad spectrum of activity and has been used to treat bacterial infections of the bone, skin, urinary tract, and lower respiratory tract. Notable species include Bacteroides, Streptococcus, and Escherichia. The following represents MIC susceptibility data for a few medically significant bacteria.
- Escherichia coli: 0.06 μg/mL
- Bacteroides fragilis: ≤0.06 μg/mL - 512 μg/mL
- Clostridium perfringens: 1 μg/mL - 4 μg/mL
References
- Stork CM (2006). "Antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals". In Nelson LH, Flomenbaum N, Goldfrank LR, Hoffman RL, Howland MD, Lewin NA (eds.). Goldfrank's toxicologic emergencies. New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 847. ISBN 0-07-143763-0. Retrieved 2009-07-03.
- "Cefotetan Susceptibility and Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Data" (PDF). Toku-e.
External links
- Cefotan official web site run by AstraZeneca US
- Cefotetan entry in RxList