 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 7–27 hours |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
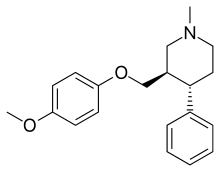
| Formula | C20H25NO2 |
| Molar mass | 311.425 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Femoxetine (INN; tentative brand name Malexil; developmental code name FG-4963) is a drug related to paroxetine that was being developed as an antidepressant by Danish pharmaceutical company Ferrosan in 1975 before acquisition of the company by Novo Nordisk. It acts as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). Development was halted to focus attention on paroxetine instead, as femoxetine could not be administered as a daily pill.
Both femoxetine and paroxetine were invented in the 1970s. Jørgen Anders Christensen's name is on the patents and Jorgen Buus-Lassen's name is on the pharmacology paper.
After Ferrosan's acquisition, femoxetine died from neglect.
In a separate patent, Ferrosan stated that Femoxetine could be used as an appetite suppressant, using ten times the dosage than for paroxetine, 300 - 400mg daily.
Femoxetine has the same stereochemical properties as Nocaine, another agent with a similar structure claimed to have been synthesized using arecoline as the starting alkaloid.
Analogs
| This section may be too technical for most readers to understand. Please help improve it to make it understandable to non-experts, without removing the technical details. (March 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
- Addition of the para-fluoro atom results in a different compound that is a hybrid of femoxetine & paroxetine named FG 7080, which has a separate patent. According to the patent tables, incorporation of the fluorine atom potentiated the 5-HT affinity considerably.
- Pfizer made some similar analogs E.g. a Viloxazine type of catechol ether is used, but 4-phenyl instead of based on a morpholine ring.
- NNC-63-0780. binds to ORL1 instead of SERT.
- NNC 09-0026
See also
References
- U.S. patent 3,912,743
- U.S. patent 4,007,196
- Lassen JB, Petersen E, Kjellberg B, Olsson SO (May 1975). "Comparative studies of a new 5HT-uptake inhibitor and some tricyclic thymoleptics". European Journal of Pharmacology. 32 (1): 108–15. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(75)90329-5. PMID 1149822.
- Healy D (2004). Let them eat Prozac: the unhealthy relationship between the pharmaceutical industry and depression. New York, NY: New York Univ. Press. pp. 26–27. ISBN 9780814736692.
Jørgen Buus Lassen femoxetine.
- U.S. patent 4,442,113
- "(3S,4R)-4-(4-Fluorophenyl)-3-[(4-methoxyphenoxy)methyl]piperidine". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- U.S. patent 4,585,777
- U.S. patent 20,070,142,389
- Bignan GC, Connolly PJ, Middleton SA (2005). "Recent advances towards the discovery of ORL-1 receptor agonists and antagonists". Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents. 15 (4): 357–388 6. doi:10.1517/13543776.15.4.357. S2CID 94720416.
- "CID:9862655". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
| Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor modulators | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAChRsTooltip Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors |
| ||||
| Precursors (and prodrugs) | |||||
This drug article relating to the nervous system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |