| Revision as of 16:22, 19 January 2012 editCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'ChemSpiderID_Ref', 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref', 'StdInChI_Ref', 'StdInChIKey_Ref', 'CASNo_Ref') per [[WP:CHEMVALID|Chem/Drugbox validat...← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 04:00, 23 November 2024 edit undoCitation bot (talk | contribs)Bots5,435,876 edits Removed parameters. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Graeme Bartlett | #UCB_toolbar | ||
| (60 intermediate revisions by 41 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{chembox | {{chembox | ||
| | Watchedfields = changed | |||
| | verifiedrevid = 427708720 | | verifiedrevid = 427708720 | ||
| | ImageFile = Boron-phosphide-unit-cell-1963-CM-3D-balls.png | | ImageFile = Boron-phosphide-unit-cell-1963-CM-3D-balls.png | ||
| | ImageSize = |
| ImageSize = | ||
| | IUPACName = |
| IUPACName = | ||
| | OtherNames = |
| OtherNames = | ||
| | |
|Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | ||
| | CASNo = 20205-91-8 | | CASNo = 20205-91-8 | ||
| | ChemSpiderID = 79763 | |||
| | EC_number = 243-593-3 | |||
| | PubChem = 88409 | | PubChem = 88409 | ||
| | StdInChI=1S/BP/c1-2 | |||
| | SMILES = | |||
| | StdInChIKey = FFBGYFUYJVKRNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||
| | SMILES1 = . | |||
| | SMILES2 = B#P | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| | |
|Section2={{Chembox Properties | ||
| | Formula = BP | | Formula = BP | ||
| | MolarMass = 41.7855 g/mol | | MolarMass = 41.7855 g/mol | ||
| | Appearance = maroon powder | | Appearance = maroon powder | ||
| | Density = 2.90 g/cm<sup>3</sup> | | Density = 2.90 g/cm<sup>3</sup> | ||
| | |
| MeltingPtC = 1100 | ||
| | MeltingPt_notes = (decomposes) | |||
| | BoilingPt = | |||
| | |
| BoilingPt = | ||
| | Solubility = | |||
| | BandGap = 2 eV (indirect) | |||
| | BandGap = 2.1 eV (indirect, 300 K)<ref name=Madelung>{{cite book | author = Madelung, O. | title = Semiconductors: Data Handbook | year = 2004 | publisher = Birkhäuser | isbn = 978-3-540-40488-0 | pages = 84–86 | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=v_8sMfNAcA4C&pg=PA84 }}</ref> | |||
| | ElectronMobility = 5400 cm<sup>2</sup>/(V*s) (300 K) | |||
| | ThermalConductivity = 4 W/(cm |
| ThermalConductivity = 4.6 W/(cm·K) (300 K)<ref name=bpthermal/> | ||
| | RefractIndex = 3. |
| RefractIndex = 3.0 (0.63 μm)<ref name=Madelung/> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| | |
|Section3={{Chembox Structure | ||
| | |
| SpaceGroup = F{{overline|4}}3m | ||
| | |
| CrystalStruct = ] | ||
| | |
| Coordination = Tetrahedral | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| | |
|Section7={{Chembox Hazards | ||
| | MainHazards = |
| MainHazards = | ||
| | FlashPt = |
| FlashPt = | ||
| | |
| AutoignitionPt = | ||
| ⚫ | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| ⚫ | '''Boron phosphide''' (BP) (also referred to as boron monophosphide, to distinguish it from boron subphosphide, B<sub>12</sub>P<sub>2</sub>) is a chemical compound of ] and ]. It is a ].<ref>{{cite journal |author1=Popper, P. |author2=Ingles, T. A. | title = Boron Phosphide, a III–V Compound of Zinc-Blende Structure | journal = Nature | year = 1957 | volume = 179 |issue=4569 | page = 1075 | doi = 10.1038/1791075a0 |bibcode=1957Natur.179.1075P | doi-access = free }}</ref> | ||
| ⚫ | }} | ||
| ⚫ | '''Boron phosphide''' (BP) (also referred to as boron monophosphide, to distinguish it from boron subphosphide |
||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
| Crystals of boron phosphide were synthesized by ] as early as |
Crystals of boron phosphide were synthesized by ] as early as 1891.<ref>{{cite journal | author = Moissan, H. | title = Préparation et Propriétés des Phosphures de Bore | journal = Comptes Rendus | volume = 113 | year = 1891 | pages = 726–729 | url = http://visualiseur.bnf.fr/CadresFenetre?O=NUMM-3069&I=726&M=tdm }}</ref> | ||
| ==Appearance== | ==Appearance== | ||
| Pure BP is almost transparent, n-type crystals are orange-red whereas p-type ones are dark red |
Pure BP is almost transparent, n-type crystals are orange-red whereas p-type ones are dark red.<ref name=berger>{{cite book | author = Berger, L. I. | title = Semiconductor Materials | publisher = CRC Press | year = 1996 | isbn = 978-0-8493-8912-2 | url = https://archive.org/details/semiconductormat0000berg | url-access = registration | page = }}</ref> | ||
| ==Chemical properties== | ==Chemical properties== | ||
| BP is not attacked by acids or boiling aqueous alkali water solutions. It is only attacked by molten alkalis.<ref name=berger/> |
BP is not attacked by acids or boiling aqueous alkali water solutions. It is only attacked by molten alkalis.<ref name=berger/> | ||
| ==Physical properties |
==Physical properties== | ||
| BP is known to be chemically inert and exhibit very high thermal conductivity.<ref name=bpthermal>{{cite journal |author1=Kang, J. |author2=Wu, H. | author3=Hu, Y.| title = Thermal Properties and Phonon Spectral Characterization of Synthetic Boron Phosphide for High Thermal Conductivity Applications | journal = Nano Letters| year = 2017 | volume = 17 |issue=12 |pages=7507–7514 | doi = 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b03437 | pmid = 29115845 |bibcode=2017NanoL..17.7507K }}</ref> Some properties of BP are listed below: | |||
| ⚫ | *coefficient of thermal expansion |
||
| * lattice constant 0.45383 nm | |||
| ⚫ | *heat capacity C<sub>P</sub> ~ 0.8 J/(g |
||
| ⚫ | * coefficient of thermal expansion 3.65{{e|−6}} /°C (400 K) | ||
| ⚫ | *Debye temperature = |
||
| ⚫ | * heat capacity C<sub>P</sub> ~ 0.8 J/(g·K) (300 K) | ||
| ⚫ | *relatively high microhardness of 32 GPa (100 g load). | ||
| ⚫ | * Debye temperature = 985 K | ||
| ⚫ | *electron and hole mobilities of few hundred cm<sup>2</sup>/(V |
||
| * ] 152 GPa | |||
| ⚫ | * relatively high microhardness of 32 GPa (100 g load). | ||
| ⚫ | * electron and hole mobilities of a few hundred cm<sup>2</sup>/(V·s) (up to 500 for holes at 300 K) | ||
| * high thermal conductivity of ~ 460 W/(m·K) at room temperature<ref name=bpthermal/> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| ===Related materials=== | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| Line 63: | Line 72: | ||
| {{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| * |
* {{cite book | title = Boron Chemistry at the Millennium | editor = King, R. B. | publisher = Elsevier Science & Technology | year = 1999 | isbn = 0-444-72006-5 }} | ||
| * P-n junction type boron phosphide-based semiconductor light-emitting device and production method thereof, United States Patent 6831304 | |||
| * {{cite patent | status = patent | title = P-N Junction Type Boron Phosphide-Based Semiconductor Light-Emitting Device and Production Method thereof | country = US | number = 6831304 | gdate = 2004-12-14 | assign1 = Showa Denko | inventor = Takashi, U. }} | |||
| * Semiconducting Properties of Cubic Boron Phosphide, B. Stone and D. Hill, Phys. Rev. Lett. vol. 4, 282–284 (1960) {{doi|10.1103/PhysRevLett.4.282}} | |||
| * {{cite journal | title = Semiconducting Properties of Cubic Boron Phosphide |author1=Stone, B. |author2=Hill, D. | journal = Physical Review Letters | year = 1960 | volume = 4 | issue = 6 | pages = 282–284 | doi = 10.1103/PhysRevLett.4.282 | bibcode = 1960PhRvL...4..282S }} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{Boron compounds}} | {{Boron compounds}} | ||
| {{Phosphorus compounds}} | |||
| {{Phosphides}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Boron Phosphide}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Boron Phosphide}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| {{inorganic-compound-stub}} | {{inorganic-compound-stub}} | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 04:00, 23 November 2024
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.039.616 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | BP |
| Molar mass | 41.7855 g/mol |
| Appearance | maroon powder |
| Density | 2.90 g/cm |
| Melting point | 1,100 °C (2,010 °F; 1,370 K) (decomposes) |
| Band gap | 2.1 eV (indirect, 300 K) |
| Thermal conductivity | 4.6 W/(cm·K) (300 K) |
| Refractive index (nD) | 3.0 (0.63 μm) |
| Structure | |
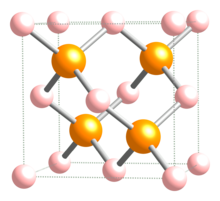
| Crystal structure | Zinc blende |
| Space group | F43m |
| Coordination geometry | Tetrahedral |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Boron phosphide (BP) (also referred to as boron monophosphide, to distinguish it from boron subphosphide, B12P2) is a chemical compound of boron and phosphorus. It is a semiconductor.
History
Crystals of boron phosphide were synthesized by Henri Moissan as early as 1891.
Appearance
Pure BP is almost transparent, n-type crystals are orange-red whereas p-type ones are dark red.
Chemical properties
BP is not attacked by acids or boiling aqueous alkali water solutions. It is only attacked by molten alkalis.
Physical properties
BP is known to be chemically inert and exhibit very high thermal conductivity. Some properties of BP are listed below:
- lattice constant 0.45383 nm
- coefficient of thermal expansion 3.65×10 /°C (400 K)
- heat capacity CP ~ 0.8 J/(g·K) (300 K)
- Debye temperature = 985 K
- Bulk modulus 152 GPa
- relatively high microhardness of 32 GPa (100 g load).
- electron and hole mobilities of a few hundred cm/(V·s) (up to 500 for holes at 300 K)
- high thermal conductivity of ~ 460 W/(m·K) at room temperature
See also
References
- ^ Madelung, O. (2004). Semiconductors: Data Handbook. Birkhäuser. pp. 84–86. ISBN 978-3-540-40488-0.
- ^ Kang, J.; Wu, H.; Hu, Y. (2017). "Thermal Properties and Phonon Spectral Characterization of Synthetic Boron Phosphide for High Thermal Conductivity Applications". Nano Letters. 17 (12): 7507–7514. Bibcode:2017NanoL..17.7507K. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b03437. PMID 29115845.
- Popper, P.; Ingles, T. A. (1957). "Boron Phosphide, a III–V Compound of Zinc-Blende Structure". Nature. 179 (4569): 1075. Bibcode:1957Natur.179.1075P. doi:10.1038/1791075a0.
- Moissan, H. (1891). "Préparation et Propriétés des Phosphures de Bore". Comptes Rendus. 113: 726–729.
- ^ Berger, L. I. (1996). Semiconductor Materials. CRC Press. p. 116. ISBN 978-0-8493-8912-2.
Further reading
- King, R. B., ed. (1999). Boron Chemistry at the Millennium. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN 0-444-72006-5.
- US patent 6831304, Takashi, U., "P-N Junction Type Boron Phosphide-Based Semiconductor Light-Emitting Device and Production Method thereof", issued 2004-12-14, assigned to Showa Denko
- Stone, B.; Hill, D. (1960). "Semiconducting Properties of Cubic Boron Phosphide". Physical Review Letters. 4 (6): 282–284. Bibcode:1960PhRvL...4..282S. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.4.282.
| Boron compounds | |
|---|---|
| Boron pnictogenides | |
| Boron halides | |
| Acids | |
| Boranes | |
| Boron oxides and sulfides | |
| Carbides | |
| Organoboron compounds | |
| Phosphorus compounds | |
|---|---|
| Phosphides | |
| Other compounds | |
| Phosphides | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binary phosphides |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ternary phosphides | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quaternary phosphides | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quinary phosphides | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| See also | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This inorganic compound–related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |