| Revision as of 18:34, 20 November 2011 editRjwilmsiBot (talk | contribs)Bots, Pending changes reviewers1,602,950 editsm →Pharmacological effects: fixing page range dashes using AWB (7863)← Previous edit | Revision as of 08:05, 21 November 2011 edit undoWikitanvirBot (talk | contribs)144,145 editsm r2.7.1) (Robot: Modifying fi:Hupertsiini ANext edit → | ||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Revision as of 08:05, 21 November 2011
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
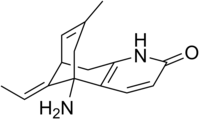
| IUPAC name (1R,9S,13E)- 1-Amino- 13-ethylidene- 11-methyl- 6-azatricyclo trideca- 2(7),3,10- trien- 5-one | |
| Other names HupA | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.132.430 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C15H18N2O |
| Molar mass | 242.32 g/mol |
| Melting point | 217–219 °C |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Huperzine A is a naturally occurring sesquiterpene alkaloid compound found in the plant firmoss Huperzia serrata.
Huperzine A is also an Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, which has a mechanism of action similar to donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine. A pro-drug form of Huperzine A (ZT-1) is under development as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease.
In the US, Huperzine A is sold as a dietary supplement for memory support. The botanical has been used in China for centuries for the treatment of swelling, fever and blood disorders. Clinical trials in China have shown it to be effective in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and enhancing memory in students.
Pharmacological effects
Huperzine A is an acetylcholinesterase inhibititor and NMDA receptor antagonist,.
Huperzine A has also attracted the attention of US medical science. It is currently being investigated as a possible treatment for diseases characterized by neurodegeneration – particularly Alzheimer's disease. It has been found to be an inhibitor of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. The structure of the complex of huperzine A with acetylcholinesterase has been determined. by X-ray crystallography (PDB code: 1VOT; see the 3D structure).This is the same mechanism of action of pharmaceutical drugs such as galantamine and donepezil used to treat Alzheimer's disease. Huperzine A is also a NMDA receptor antagonist which protects the brain against glutamate induced damage, and it appears to increase nerve growth factor levels in rats.
Clinical trials in China have shown that huperzine A is comparably effective to similar drugs on the market, and may even be a bit safer in terms of side effects. The National Institute on Aging has completed a Phase II clinical trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of huperzine A in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease in a randomized controlled trial of its effect on cognitive function.The study concluded that huperzine A 200 mug BID has no demonstrable cognitive effect in patients with mild to moderate AD.
Possible side effects include breathing problems, tightness in the throat or chest, chest pain, skin hives, rash, itchy or swollen skin, upset stomach, diarrhea, vomiting, hyperactivity and insomnia. Most adverse events were cholinergic in nature and no serious adverse events occurred. Huperzine A is a well-tolerated drug.
See also
References
- Kozikowski, Alan P.; Tueckmantel, Werner (1999). "Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Clinical Efficacy of the Chinese Nootropic Agent Huperzine A". Accounts of Chemical Research. 32 (8): 641–650. doi:10.1021/ar9800892.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - P. Scalfaro, V. Nicolas, M.P. Simonin, S. Charbon, M. McCormick, F. Heimgartner. The sustained release of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor ZT-1 confers the potential for a more efficient neuroprotection in rats. Neurobiology of Aging Conference in New Orleans, Nov 2003.
- ^ Wang, Bai-Song; Wang, Hao; Wei, Zhao-hui; Song, Yan-yan; Zhang, Lu; Chen, Hong-Zhuan (2009). "Efficacy and safety of natural acetylcholinesterase inhibitor huperzine A in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: an updated meta-analysis". Journal of Neural Transmission. 116 (4): 457. doi:10.1007/s00702-009-0189-x. PMID 19221692.
- Sun, QQ; Xu, SS; Pan, JL; Guo, HM; Cao, WQ (1999). "Huperzine-A capsules enhance memory and learning performance in 34 pairs of matched adolescent students". Zhongguo yao li xue bao = Acta pharmacologica Sinica. 20 (7): 601–3. PMID 10678121.
- ^ Wang, BS; Wang, H; Wei, ZH; Song, YY; Zhang, L; Chen, HZ (2009). "Efficacy and safety of natural acetylcholinesterase inhibitor huperzine A in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: an updated meta-analysis". Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996). 116 (4): 457–65. doi:10.1007/s00702-009-0189-x. PMID 19221692.
- Coleman, BR; Ratcliffe, RH; Oguntayo, SA; Shi, X; Doctor, BP; Gordon, RK; Nambiar, MP (2008). "+-Huperzine A treatment protects against N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced seizure/status epilepticus in rats". Chemico-biological interactions. 175 (1–3): 387–95. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2008.05.023. PMID 18588864.
- Zangara, A (2003). "The psychopharmacology of huperzine A: an alkaloid with cognitive enhancing and neuroprotective properties of interest in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease". Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 75 (3): 675–86. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(03)00111-4. PMID 12895686.
- ^ Bai, D. L.; Tang, X. C.; He, X. C. (2000). "Huperzine A, a potential therapeutic agent for treatment of Alzheimer's disease". Current Medicinal Chemistry. 7 (3): 355–374. PMID 10637369.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Tang, X. C.; He, X. C.; Bai, D. L. (1999). "Huperzine A: a novel acetylcholinesterase inhibitor". Drugs of the Future. 24 (6): 647–663. doi:10.1358/dof.1999.024.06.545143.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Raves, ML; Harel, M; Pang, Y-P; Silman, I; Kozikowski, AP; Sussman, JL (1997). "3D structure of acetylcholinesterase complexed with the nootropic alkaloid, (-)-huperzine A.". Nature Struct Biol. 4 (1): 57–63. PMID 8989325.
- Tang, L., Wang, R., Tang, X. (2005). "Effects of huperzine A on secretion of nerve growth factor in cultured rat cortical astrocytes and neurite outgrowth in rat PC12 cells". Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 26 (6): 673–678. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7254.2005.00130.x. PMID 15916732.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Huperzine A, Alzherimer Research Forum
- Rafii M.S., Walsh S., Little J.T., Behan K., Reynolds B., Ward C., Jin S., Thomas R., Aisen P.S.,"A phase II trial of huperzine A in mild to moderate Alzheimer disease". Neurology. 76 (16) (pp 1389-1394), 2011.