| Revision as of 20:53, 10 August 2018 editJay Hodec (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users5,833 editsmNo edit summaryTag: Visual edit← Previous edit | Revision as of 23:44, 2 June 2019 edit undoAmericanLemming (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users13,776 edits capitalization and italicsNext edit → | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
| '''Isocarboxazid''' ('''Marplan''', '''Marplon''', '''Enerzer''') is a non-selective, ] ] (MAOI) of the ] class used as an ].<ref name="pmid2870717">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fagervall I, Ross SB |title=Inhibition of monoamine oxidase in monoaminergic neurones in the rat brain by irreversible inhibitors |journal=] |volume=35 |issue=8 |pages=1381–7 |date=April 1986 |pmid=2870717 |doi= 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90285-6|url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/0006-2952(86)90285-6}}</ref> Along with ] and ], it is one of only three classical MAOIs still available for clinical use in the treatment of psychiatric disorders in the ],<ref name="Rosenberg2013">{{cite book|author=David Rosenberg|title=Pocket Guide For The Textbook Of Pharmacotherapy For Child And Adolescent Psychiatric Disorders|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fep_AAAAQBAJ&pg=PA176|date=21 August 2013|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-1-134-86002-9|pages=176–}}</ref><ref name="LabbateFava2012">{{cite book|author1=Lawrence A. Labbate|author2=Maurizio Fava|author3=Jerrold F. Rosenbaum|author4=George W. Arana|title=Handbook of Psychiatric Drug Therapy|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=xrZfcE8MydIC&pg=PA99|date=28 March 2012|publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins|isbn=978-1-4511-5307-1|pages=99–}}</ref> though it is not as commonly employed in comparison to the others.<ref name="Rosenberg2013" /><ref name="LabbateFava2012" /> | '''Isocarboxazid''' ('''Marplan''', '''Marplon''', '''Enerzer''') is a non-selective, ] ] (MAOI) of the ] class used as an ].<ref name="pmid2870717">{{cite journal |vauthors=Fagervall I, Ross SB |title=Inhibition of monoamine oxidase in monoaminergic neurones in the rat brain by irreversible inhibitors |journal=] |volume=35 |issue=8 |pages=1381–7 |date=April 1986 |pmid=2870717 |doi= 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90285-6|url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/0006-2952(86)90285-6}}</ref> Along with ] and ], it is one of only three classical MAOIs still available for clinical use in the treatment of psychiatric disorders in the ],<ref name="Rosenberg2013">{{cite book|author=David Rosenberg|title=Pocket Guide For The Textbook Of Pharmacotherapy For Child And Adolescent Psychiatric Disorders|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fep_AAAAQBAJ&pg=PA176|date=21 August 2013|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-1-134-86002-9|pages=176–}}</ref><ref name="LabbateFava2012">{{cite book|author1=Lawrence A. Labbate|author2=Maurizio Fava|author3=Jerrold F. Rosenbaum|author4=George W. Arana|title=Handbook of Psychiatric Drug Therapy|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=xrZfcE8MydIC&pg=PA99|date=28 March 2012|publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins|isbn=978-1-4511-5307-1|pages=99–}}</ref> though it is not as commonly employed in comparison to the others.<ref name="Rosenberg2013" /><ref name="LabbateFava2012" /> | ||
| Isocarboxazid is primarily used to treat ] and ]s. It has also been investigated in the treatment of ] and other ]-related disorders. Isocarboxazid may produce ]s, ], ], and minor anticholinergic ].<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Larsen JK, Krogh-Nielsen L, Brøsen K |title=The Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Isocarboxazid is a Relevant Treatment Option in Treatment-Resistant Depression |journal=Health Care: Current Reviews |volume=4|issue=2 |date=April 2016 | url=https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/50716122.pdf}}</ref> Isocarboxazid, as well as other MAOIs, increase the levels of the ] ] ], ], and ] in the brain.<ref>Volz, Hanz-Peter. (November 1998) “Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors A Perspective on Their Use in The Elderly” Biochemical |
Isocarboxazid is primarily used to treat ] and ]s. It has also been investigated in the treatment of ] and other ]-related disorders. Isocarboxazid may produce ]s, ], ], and minor anticholinergic ].<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Larsen JK, Krogh-Nielsen L, Brøsen K |title=The Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Isocarboxazid is a Relevant Treatment Option in Treatment-Resistant Depression |journal=Health Care: Current Reviews |volume=4|issue=2 |date=April 2016 | url=https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/50716122.pdf}}</ref> Isocarboxazid, as well as other MAOIs, increase the levels of the ] ] ], ], and ] in the brain.<ref>Volz, Hanz-Peter. (November 1998) “Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors A Perspective on Their Use in The Elderly” ''Biochemical Pharmacology'' (5) 341-352.</ref> | ||
| Classical MAOIs, including isocarboxazid, are used only very rarely due to prominent ] and ]s and have been largely superseded by newer antidepressants such as the ]s (SSRIs). The cause of the interactions is because MAOIs inhibit the ] of dietary amines (e.g., ]) and the monoamine neurotransmitters. In combination with other drugs that increase the levels of the monoamine neurotransmitters such as the SSRIs, or with certain foods high in dietary amines such as ]s, MAOIs can produce dangerous elevations of monoamine neurotransmitters resulting in potentially life-threatening syndromes such as ] and ]. | Classical MAOIs, including isocarboxazid, are used only very rarely due to prominent ] and ]s and have been largely superseded by newer antidepressants such as the ]s (SSRIs). The cause of the interactions is because MAOIs inhibit the ] of dietary amines (e.g., ]) and the monoamine neurotransmitters. In combination with other drugs that increase the levels of the monoamine neurotransmitters such as the SSRIs, or with certain foods high in dietary amines such as ]s, MAOIs can produce dangerous elevations of monoamine neurotransmitters resulting in potentially life-threatening syndromes such as ] and ]. | ||
Revision as of 23:44, 2 June 2019
Pharmaceutical compound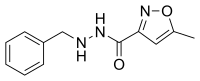 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Marplan |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| MedlinePlus | a605036 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | ? |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.399 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H13N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 231.25 g/mol g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Isocarboxazid (Marplan, Marplon, Enerzer) is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class used as an antidepressant. Along with phenelzine and tranylcypromine, it is one of only three classical MAOIs still available for clinical use in the treatment of psychiatric disorders in the United States, though it is not as commonly employed in comparison to the others.
Isocarboxazid is primarily used to treat mood and anxiety disorders. It has also been investigated in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and other dementia-related disorders. Isocarboxazid may produce headaches, orthostatic hypotension, dizziness, and minor anticholinergic side effects. Isocarboxazid, as well as other MAOIs, increase the levels of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine in the brain.
Classical MAOIs, including isocarboxazid, are used only very rarely due to prominent food and drug interactions and have been largely superseded by newer antidepressants such as the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). The cause of the interactions is because MAOIs inhibit the metabolism of dietary amines (e.g., tyramine) and the monoamine neurotransmitters. In combination with other drugs that increase the levels of the monoamine neurotransmitters such as the SSRIs, or with certain foods high in dietary amines such as aged cheeses, MAOIs can produce dangerous elevations of monoamine neurotransmitters resulting in potentially life-threatening syndromes such as hypertensive crisis and serotonin syndrome.
See also
References
- "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- Fagervall I, Ross SB (April 1986). "Inhibition of monoamine oxidase in monoaminergic neurones in the rat brain by irreversible inhibitors". Biochemical pharmacology. 35 (8): 1381–7. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(86)90285-6. PMID 2870717.
- ^ David Rosenberg (21 August 2013). Pocket Guide For The Textbook Of Pharmacotherapy For Child And Adolescent Psychiatric Disorders. Routledge. pp. 176–. ISBN 978-1-134-86002-9.
- ^ Lawrence A. Labbate; Maurizio Fava; Jerrold F. Rosenbaum; George W. Arana (28 March 2012). Handbook of Psychiatric Drug Therapy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 99–. ISBN 978-1-4511-5307-1.
- Larsen JK, Krogh-Nielsen L, Brøsen K (April 2016). "The Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Isocarboxazid is a Relevant Treatment Option in Treatment-Resistant Depression" (PDF). Health Care: Current Reviews. 4 (2).
- Volz, Hanz-Peter. (November 1998) “Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors A Perspective on Their Use in The Elderly” Biochemical Pharmacology (5) 341-352.
| Monoamine metabolism modulators | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-specific |
| ||||||||||
| Phenethylamines (dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine) |
| ||||||||||
| Tryptamines (serotonin, melatonin) |
| ||||||||||
| Histamine |
| ||||||||||
| See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Adrenergics • Dopaminergics • Melatonergics • Serotonergics • Monoamine reuptake inhibitors • Monoamine releasing agents • Monoamine neurotoxins | |||||||||||
| Hydrazines | |
|---|---|
|