This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Beetstra (talk | contribs) at 11:32, 7 November 2011 (Script assisted update of identifiers for the Chem/Drugbox validation project (updated: '').). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 11:32, 7 November 2011 by Beetstra (talk | contribs) (Script assisted update of identifiers for the Chem/Drugbox validation project (updated: '').)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Pharmaceutical compound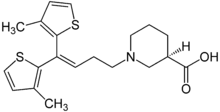 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Gabitril |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a698014 |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 90% |
| Protein binding | 96% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP450 system) |
| Elimination half-life | 7-9 hours |
| Excretion | Fecal and renal |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H25NO2S2 |
| Molar mass | 375.55 g/mol g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Tiagabine (/taɪˈæɡəbiːn/ is an anti-convulsive medication produced by Cephalon and marketed under the brand name Gabitril. The drug was discovered at Novo Nordisk in Denmark in 1988 and was co-developed with Abbott. After a period of co-promotion, Cephalon licensed Tiagabine from Abbott/Novo and now is the exclusive producer. The medication is also used in the treatment of panic disorder, as are a few other anticonvulsants.
Indications
Tiagabine is approved by U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as an adjunctive treatment for partial seizures in ages 12 and up. It may also be prescribed to treat anxiety disorders and neuropathic pain (including fibromyalgia). For anxiety and neuropathic pain, tiagabine is used primarily to augment other treatments. Tiagabine may be used alongside SSRIs, SNRIs or benzodiazepines for anxiety, or antidepressants, gabapentin, anticonvulsants or opiates for neuropathic pain.
Pharmacology
It is believed that the pharmacology is related to its ability, documented in in vitro experiments, to enhance the activity of gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. These experiments have shown that tiagabine binds to recognition sites associated with the GABA uptake carrier. It is thought that, by this action, tiagabine blocks GABA uptake into presynaptic neurons, permitting more GABA to be available for receptor binding on the surfaces of post-synaptic cells. Evidence is available that it operates as a selective GABA reuptake inhibitor.
Side effects
Tiagabine's most common side effects include confusion, difficulty speaking clearly/stuttering, mild sedation, and in doses over 8 mg, a tingling sensation (paresthesia) in the body's extremities, particularly the hands and fingers. Tiagabine may induce seizures in those without epilepsy, especially if they are taking another drug which lowers the seizure threshold.
With overdoses in the range of 20-40 mg or more it will cause extreme sedation, temporary retardation, muscle tremors and spasms, uncontrollable bodily tremors, retrograde and anterograde amnesia, thrashing, screaming, flailing and extreme hostility, unconsciousness with seizures or seizure-like symptoms. Upon consciousness: extreme confusion with an inability to form coherent sentences, express ideas, or do the most basic activities for several hours. Unlike the benzodiazepines Tiagabine (Gabitril) has been shown to have no recreation value and any euphoria is most likely a placebo effect or because of consumption with alcohol.
Synthesis
Andersen, Knud Erik; Braestrup, Claus; Groenwald, Frederik C.; Joergensen, Anker S.; Nielsen, Erik B.; Sonnewald, Ursula; Soerensen, Per O.; Suzdak, Peter D.; Knutsen, Lars J. S. (1993). "The synthesis of novel GABA uptake inhibitors. 1. Elucidation of the structure-activity studies leading to the choice of (R)-1--3-piperidinecarboxylic acid (Tiagabine) as an anticonvulsant drug candidate". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 36 (12): 1716. doi:10.1021/jm00064a005. PMID 8510100.
References
- ^ Stahl, S. Stahl's Essential Psychopharmacology: Prescriber's Guide. Cambridge University Press: New York, NY. 2009. pp. 523-526
- Pollack MH, Roy-Byrne PP, Van Ameringen M; et al. (2005). "The selective GABA reuptake inhibitor tiagabine for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: results of a placebo-controlled study". The Journal of clinical psychiatry. 66 (11): 1401–8. doi:10.4088/JCP.v66n1109. PMID 16420077.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
External links
- Gabitril (manufacturer's website)
- Pharmacology
| Anxiolytics (N05B) | |
|---|---|
| 5-HT1ARTooltip 5-HT1A receptor agonists | |
| GABAARTooltip GABAA receptor PAMsTooltip positive allosteric modulators |
|
| Hypnotics | |
| Gabapentinoids (α2δ VDCC blockers) | |
| Antidepressants |
|
| Antipsychotics | |
| Sympatholytics (Antiadrenergics) |
|
| Others | |
| |
| Mood stabilizers | |
|---|---|
| Anticonvulsants | |
| Atypical antipsychotics | |
| Others | |
| Mood disorder | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectrum |
| ||||||||
| Symptoms | |||||||||
| Diagnosis | |||||||||
| Treatment |
| ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
| GABA receptor modulators | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ionotropic |
| ||||
| Metabotropic |
| ||||
