| |||
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name Acetone | |||
| Preferred IUPAC name Propan-2-one | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name 2-Propanone | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| Beilstein Reference | 635680 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.602 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| Gmelin Reference | 1466 | ||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Acetone | ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1090 | ||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C3H6O | ||
| Molar mass | 58.080 g·mol | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Odor | Pungent, fruity | ||
| Density | 0.7845 g/cm (25 °C) | ||
| Melting point | −94.9 °C (−138.8 °F; 178.2 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 56.08 °C (132.94 °F; 329.23 K) | ||
| Solubility in water | Miscible | ||
| Solubility | Miscible in benzene, diethyl ether, methanol, chloroform, ethanol | ||
| log P | −0.24 | ||
| Vapor pressure |
| ||
| Acidity (pKa) |
| ||
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | −33.8·10 cm/mol | ||
| Thermal conductivity | 0.161 W/(m·K) (25 °C) | ||
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.3588 (20 °C) | ||
| Viscosity | 0.306 mPa·s (25 °C) | ||
| Structure | |||
| Coordination geometry | Trigonal planar at C2 | ||
| Molecular shape | Dihedral at C2 | ||
| Dipole moment | 2.88 D | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Heat capacity (C) | 126.3 J/(mol·K) | ||
| Std molar entropy (S298) |
199.8 J/(mol·K) | ||
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH298) |
−248.4 kJ/mol | ||
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH298) |
−1.79 MJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
| Main hazards | Highly flammable | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| Pictograms |  
| ||
| Signal word | Danger | ||
| Hazard statements | H225, H302, H319, H336, H373 | ||
| Precautionary statements | P210, P235, P260, P305+P351+P338 | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 | ||
| Flash point | −20 °C (−4 °F; 253 K) | ||
| Autoignition temperature |
465 °C (869 °F; 738 K) | ||
| Explosive limits | 2.5–12.8% | ||
| Threshold limit value (TLV) | 250 ppm (STEL), 500 ppm (C) | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
| LD50 (median dose) |
| ||
| LC50 (median concentration) | 20,702 ppm (rat, 8 h) | ||
| LCLo (lowest published) | 45,455 ppm (mouse, 1 h) | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
| PEL (Permissible) | 1000 ppm (2400 mg/m) | ||
| REL (Recommended) | TWA 250 ppm (590 mg/m) | ||
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | 2500 ppm | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related compounds | |||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Acetone (data page) | |||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
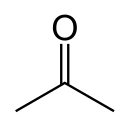
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CO. It is the simplest and smallest ketone (>C=O). It is a colorless, highly volatile, and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour, very reminiscent of the smell of pear drops.
Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important organic solvent in industry, home, and laboratory. About 6.7 million tonnes were produced worldwide in 2010, mainly for use as a solvent and for production of methyl methacrylate and bisphenol A, which are precursors to widely used plastics. It is a common building block in organic chemistry. It serves as a solvent in household products such as nail polish remover and paint thinner. It has volatile organic compound (VOC)-exempt status in the United States.
Acetone is produced and disposed of in the human body through normal metabolic processes. It is normally present in blood and urine. People with diabetic ketoacidosis produce it in larger amounts. Ketogenic diets that increase ketone bodies (acetone, β-hydroxybutyric acid and acetoacetic acid) in the blood are used to counter epileptic attacks in children who suffer from refractory epilepsy.
Name
From the 17th century, and before modern developments in organic chemistry nomenclature, acetone was given many different names. They included "spirit of Saturn", which was given when it was thought to be a compound of lead and, later, "pyro-acetic spirit" and "pyro-acetic ester".
Prior to the name "acetone" being coined by French chemists (see below), it was named "mesit" (from the Greek μεσίτης, meaning mediator) by Carl Reichenbach, who also claimed that methyl alcohol consisted of mesit and ethyl alcohol. Names derived from mesit include mesitylene and mesityl oxide which were first synthesised from acetone.
Unlike many compounds with the acet- prefix which have a 2-carbon chain, acetone has a 3-carbon chain. That has caused confusion because there cannot be a ketone with 2 carbons. The prefix refers to acetone's relation to vinegar (acetum in Latin, also the source of the words "acid" and "acetic"), rather than its chemical structure.
History
Acetone was first produced by Andreas Libavius in 1606 by distillation of lead(II) acetate.
In 1832, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas and German chemist Justus von Liebig determined the empirical formula for acetone. In 1833, French chemists Antoine Bussy and Michel Chevreul decided to name acetone by adding the suffix -one to the stem of the corresponding acid (viz, acetic acid) just as a similarly prepared product of what was then confused with margaric acid was named margarone. By 1852, English chemist Alexander William Williamson realized that acetone was methyl acetyl; the following year, the French chemist Charles Frédéric Gerhardt concurred. In 1865, the German chemist August Kekulé published the modern structural formula for acetone. Johann Josef Loschmidt had presented the structure of acetone in 1861, but his privately published booklet received little attention. During World War I, Chaim Weizmann developed the process for industrial production of acetone (Weizmann Process).
Production
In 2010, the worldwide production capacity for acetone was estimated at 6.7 million tonnes per year. With 1.56 million tonnes per year, the United States had the highest production capacity, followed by Taiwan and China. The largest producer of acetone is INEOS Phenol, owning 17% of the world's capacity, with also significant capacity (7–8%) by Mitsui, Sunoco and Shell in 2010. INEOS Phenol also owns the world's largest production site (420,000 tonnes/annum) in Beveren (Belgium). Spot price of acetone in summer 2011 was 1100–1250 USD/tonne in the United States.
Current method
Acetone is produced directly or indirectly from propene. Approximately 83% of acetone is produced via the cumene process; as a result, acetone production is tied to phenol production. In the cumene process, benzene is alkylated with propylene to produce cumene, which is oxidized by air to produce phenol and acetone:
Other processes involve the direct oxidation of propylene (Wacker-Hoechst process), or the hydration of propylene to give 2-propanol, which is oxidized (dehydrogenated) to acetone.
Older methods
Previously, acetone was produced by the dry distillation of acetates, for example calcium acetate in ketonic decarboxylation.
After that time, during World War I, acetone was produced using acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation with Clostridium acetobutylicum bacteria, which was developed by Chaim Weizmann (later the first president of Israel) in order to help the British war effort, in the preparation of Cordite. This acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation was eventually abandoned when newer methods with better yields were found.
Chemical properties
Acetone is reluctant to form a hydrate:
- (CH3)2C=O + H2O ⇌ (CH3)2C(OH)2 K = 10 M
Like most ketones, acetone exhibits the keto–enol tautomerism in which the nominal keto structure (CH3)2C=O of acetone itself is in equilibrium with the enol isomer (CH3)C(OH)=(CH2) (prop-1-en-2-ol). In acetone vapor at ambient temperature, only 2.4×10% of the molecules are in the enol form.
In the presence of suitable catalysts, two acetone molecules also combine to form the compound diacetone alcohol (CH3)C=O(CH2)C(OH)(CH3)2, which on dehydration gives mesityl oxide (CH3)C=O(CH)=C(CH3)2. This product can further combine with another acetone molecule, with loss of another molecule of water, yielding phorone and other compounds.
Acetone is a weak Lewis base that forms adducts with soft acids like I2 and hard acids like phenol. Acetone also forms complexes with divalent metals.
Under ultraviolet light, acetone fluoresces..
The flame temperature of pure acetone is 1980 °C.
Polymerisation
At its melting point (−96 °C) is claimed to polymerize to give a white elastic solid, soluble in acetone, stable for several hours at room temperature. To do so, a vapor of acetone is co-condensed with magnesium as a catalyst onto a very cold surface.
Natural occurrence
Humans exhale several milligrams of acetone per day. It arises from decarboxylation of acetoacetate. Small amounts of acetone are produced in the body by the decarboxylation of ketone bodies. Certain dietary patterns, including prolonged fasting and high-fat low-carbohydrate dieting, can produce ketosis, in which acetone is formed in body tissue. Certain health conditions, such as alcoholism and diabetes, can produce ketoacidosis, uncontrollable ketosis that leads to a sharp, and potentially fatal, increase in the acidity of the blood. Since it is a byproduct of fermentation, acetone is a byproduct of the distillery industry.
Metabolism
Acetone can then be metabolized either by CYP2E1 via methylglyoxal to D-lactate and pyruvate, and ultimately glucose/energy, or by a different pathway via propylene glycol to pyruvate, lactate, acetate (usable for energy) and propionaldehyde.
Uses
About a third of the world's acetone is used as a solvent, and a quarter is consumed as acetone cyanohydrin, a precursor to methyl methacrylate.
Chemical intermediate
Acetone is used to synthesize methyl methacrylate. It begins with the initial conversion of acetone to acetone cyanohydrin via reaction with hydrogen cyanide (HCN):
In a subsequent step, the nitrile is hydrolyzed to the unsaturated amide, which is esterified:
The third major use of acetone (about 20%) is synthesizing bisphenol A. Bisphenol A is a component of many polymers such as polycarbonates, polyurethanes, and epoxy resins. The synthesis involves the condensation of acetone with phenol:
Many millions of kilograms of acetone are consumed in the production of the solvents methyl isobutyl alcohol and methyl isobutyl ketone. These products arise via an initial aldol condensation to give diacetone alcohol.
Condensation with acetylene gives 2-methylbut-3-yn-2-ol, precursor to synthetic terpenes and terpenoids.
Solvent
Acetone is a good solvent for many plastics and some synthetic fibers. It is used for thinning polyester resin, cleaning tools used with it, and dissolving two-part epoxies and superglue before they harden. It is used as one of the volatile components of some paints and varnishes. As a heavy-duty degreaser, it is useful in the preparation of metal prior to painting or soldering, and to remove rosin flux after soldering (to prevent adhesion of dirt and electrical leakage and perhaps corrosion or for cosmetic reasons), although it may attack some electronic components, such as polystyrene capacitors.
Although itself flammable, acetone is used extensively as a solvent for the safe transportation and storage of acetylene, which cannot be safely pressurized as a pure compound. Vessels containing a porous material are first filled with acetone followed by acetylene, which dissolves into the acetone. One litre of acetone can dissolve around 250 litres of acetylene at a pressure of 10 bars (1.0 MPa).
Acetone is used as a solvent by the pharmaceutical industry and as a denaturant in denatured alcohol. Acetone is also present as an excipient in some pharmaceutical drugs.
Lab and domestic solvent
A variety of organic reactions employ acetone as a polar, aprotic solvent, e.g. the Jones oxidation.
Because acetone is cheap, volatile, and dissolves or decomposes with most laboratory chemicals, an acetone rinse is the standard technique to remove solid residues from laboratory glassware before a final wash. Despite common desiccatory use, acetone dries only via bulk displacement and dilution. It forms no azeotropes with water (see azeotrope tables). Acetone also removes certain stains from microscope slides.
Acetone freezes well below −78 °C. An acetone/dry ice mixture cools many low-temperature reactions. Make-up artists use acetone to remove skin adhesive from the netting of wigs and mustaches by immersing the item in an acetone bath, then removing the softened glue residue with a stiff brush. Acetone is a main ingredient in many nail polish removers because it breaks down nail polish. It is used for all types of nail polish removal, like gel nail polish, dip powder and acrylic nails.
Biology
Proteins precipitate in acetone. The chemical modifies peptides, both at α- or ε-amino groups, and in a poorly understood but rapid modification of certain glycine residues.
In pathology, acetone helps find lymph nodes in fatty tissues (such as the mesentery) for tumor staging. The liquid dissolves the fat and hardens the nodes, making them easier to find.
Medical
Dermatologists use acetone with alcohol for acne treatments to chemically peel dry skin. Common agents used today for chemical peeling are salicylic acid, glycolic acid, azelaic acid, 30% salicylic acid in ethanol, and trichloroacetic acid (TCA). Prior to chemexfoliation, the skin is cleaned and excess fat removed in a process called defatting. Acetone, hexachlorophene, or a combination of these agents was used in this process.
Acetone has been shown to have anticonvulsant effects in animal models of epilepsy, in the absence of toxicity, when administered in millimolar concentrations. It has been hypothesized that the high-fat low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet used clinically to control drug-resistant epilepsy in children works by elevating acetone in the brain. Because of their higher energy requirements, children have higher acetone production than most adults – and the younger the child, the higher the expected production. This indicates that children are not uniquely susceptible to acetone exposure. External exposures are small compared to the exposures associated with the ketogenic diet.
Safety
Acetone's most hazardous property is its extreme flammability. In small amounts, acetone burns with a dull blue flame; in larger amounts, fuel evaporation causes incomplete combustion and a bright yellow flame. When hotter than acetone's flash point of −20 °C (−4 °F), air mixtures of 2.5‑12.8% acetone (by volume) may explode or cause a flash fire. Vapors can flow along surfaces to distant ignition sources and flash back.
Static discharge may also ignite acetone vapors, though acetone has a very high ignition initiation energy and accidental ignition is rare. Acetone's auto-ignition temperature is the relatively high 465 °C (869 °F); moreover, auto-ignition temperature depends upon experimental conditions, such as exposure time, and has been quoted as high as 535 °C. Even pouring or spraying acetone over red-glowing coal will not ignite it, due to the high vapour concentration and the cooling effect of evaporation.
Acetone should be stored away from strong oxidizers, such as concentrated nitric and sulfuric acid mixtures. It may also explode when mixed with chloroform in the presence of a base. When oxidized without combustion, for example with hydrogen peroxide, acetone may form acetone peroxide, a highly unstable primary explosive. Acetone peroxide may be formed accidentally, e.g. when waste peroxide is poured into waste solvents.
Toxicity
Acetone occurs naturally as part of certain metabolic processes in the human body, and has been studied extensively and is believed to exhibit only slight toxicity in normal use. There is no strong evidence of chronic health effects if basic precautions are followed. It is generally recognized to have low acute and chronic toxicity if ingested and/or inhaled. Acetone is not currently regarded as a carcinogen, a mutagen, or a concern for chronic neurotoxicity effects.
Acetone can be found as an ingredient in a variety of consumer products ranging from cosmetics to processed and unprocessed foods. Acetone has been rated as a generally recognized as safe (GRAS) substance when present in drinks, baked foods, desserts, and preserves at concentrations ranging from 5 to 8 mg/L.
Acetone is however an irritant, causing mild skin and moderate-to-severe eye irritation. At high vapor concentrations, it may depress the central nervous system like many other solvents. Acute toxicity for mice by ingestion (LD50) is 3 g/kg, and by inhalation (LC50) is 44 g/m over 4 hours.
Environmental effects
Although acetone occurs naturally in the environment in plants, trees, volcanic gases, forest fires, and as a product of the breakdown of body fat, the majority of the acetone released into the environment is of industrial origin. Acetone evaporates rapidly, even from water and soil. Once in the atmosphere, it has a 22-day half-life and is degraded by UV light via photolysis (primarily into methane and ethane.) Consumption by microorganisms contributes to the dissipation of acetone in soil, animals, or waterways.
EPA classification
In 1995, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) removed acetone from the list of volatile organic compounds. The companies requesting the removal argued that it would "contribute to the achievement of several important environmental goals and would support EPA's pollution prevention efforts", and that acetone could be used as a substitute for several compounds that are listed as hazardous air pollutants (HAP) under section 112 of the Clean Air Act. In making its decision EPA conducted an extensive review of the available toxicity data on acetone, which was continued through the 2000s. It found that the evaluable "data are inadequate for an assessment of the human carcinogenic potential of acetone".
Extraterrestrial occurrence
On 30 July 2015, scientists reported that upon the first touchdown of the Philae lander on comet 67P's surface, measurements by the COSAC and Ptolemy instruments revealed sixteen organic compounds, four of which were seen for the first time on a comet, including acetamide, acetone, methyl isocyanate, and propionaldehyde.
References
- The Merck Index, 15th Ed. (2013), p. 13, Acetone Monograph 65, O'Neil: The Royal Society of Chemistry.(subscription required)
- ^ Acetone in Linstrom, Peter J.; Mallard, William G. (eds.); NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg (MD)
- ^ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0004". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Klamt, Andreas (2005). COSMO-RS: From Quantum Chemistry to Fluid Phase Thermodynamics and Drug Design. Elsevier. pp. 92–94. ISBN 978-0-444-51994-8.
- Myers, Richard L. (2007). The 100 Most Important Chemical Compounds: A Reference Guide. Greenwood. pp. 4–6. ISBN 978-0-313-08057-9.
- ^ Mel Gorman, History of acetone (1600–1850), 1962
- ChemSpider lists 'acetone' as a valid, expert-verified name for what would systematically be called 'propan-2-one'.
- Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 723. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Toxicological Profile for Acetone. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency June 2022 p. 7
- ^ Haynes, p. 3.4
- Haynes, p. 5.173
- Chiang, Yvonne; Kresge, A. Jerry; Tang, Yui S.; Wirz, Jakob (1984). "The pKa and keto-enol equilibrium constant of acetone in aqueous solution". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 106 (2): 460–462. doi:10.1021/ja00314a055.
- Bordwell, Frederick G. (1988). "Equilibrium acidities in dimethyl sulfoxide solution". Accounts of Chemical Research. 21 (12): 456–463. doi:10.1021/ar00156a004. S2CID 26624076.
- Haynes, p. 3.576
- Haynes, p. 6.254
- Haynes, p. 6.243
- Haynes, p. 9.60
- Haynes, pp. 5.3, 5.67
- ^ Haynes, p. 15.13
- ^ Haynes, p. 16.34
- ^ "Acetone". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Allen, P .W.; Bowen, H. J. M.; Sutton, L. E.; Bastiansen, O. (1952). "The molecular structure of acetone". Transactions of the Faraday Society. 48: 991. doi:10.1039/TF9524800991.
- ^ Acetone, World Petrochemicals report, January 2010
- ^ Stylianos Sifniades, Alan B. Levy, "Acetone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005.
- "Update: U.S. EPA Exempt Volatile Organic Compounds". American Coatings Association. 2018-01-30. Archived from the original on 2021-02-08. Retrieved 2019-03-20.
- Freeman, JM; Kossoff, EH; Hartman, AL (Mar 2007). "The ketogenic diet: one decade later". Pediatrics. 119 (3): 535–43. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-2447. PMID 17332207. S2CID 26629499.
- C. Reichenbach (1834) "Ueber Mesit (Essiggeist) und Holzgeist" (On mesit (spirit of vinegar) and wood spirits), Annalen der Pharmacie, vol. 10, no. 3, pages 298–314.
- ^ "Acetone". 28 September 2018.
- Libavius, Andreas (1606). Alchymia (in Latin). Frankfurt, Germany: printed by Joannes Saurius, at the expense of Peter Kopff. p. 123.
- "Aceton". Chemgapedia.
- Dumas, J. (1832) "Sur l'esprit pyro-acétique" (On pyro-acetic spirit), Annales de Chimie et de Physique, 2nd series, 49 : 208–210.
- Liebig, Justus (1832) "Sur les combinaisons produites par l'action du gas oléfiant et l'esprit acétique" (On compounds produced by the action of ethylene and acetic spirit), Annales de Chimie et de Physique, 2nd series, 49 : 146–204 (especially 193–204).
- Bussy, Antoine (1833) "De quelques Produits nouveaux obtenus par l'action des Alcalis sur les Corps gras à une haute température" (On some new products obtained by the action of alkalies on fatty substances at a high temperature), Annales de Chimie et de Physique, 2nd series, 53 : 398–412; see footnote on pp. 408–409.
- Williamson, A. W. (1852) "On Etherification," Journal of the Chemical Society, 4 : 229–239; (especially pp. 237–239).
- Gerhardt, Charles (1853) "Researches sur les acids organiques anhydres" (Research on anhydrous organic acids), Annales de Chimie et de Physique, 3rd series, 37 : 285–342; see p. 339.
- Kekulé, Auguste (1865) "Sur la constitution des substances aromatiques," Bulletin de la Société chimique de Paris, 1 : 98–110; (especially p. 110).
- Kekulé, Auguste (1866) "Untersuchungen über aromatischen Verbindungen" (Investigations into aromatic compounds), Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie, 137 : 129–196; (especially pp. 143–144).
- Loschmidt, J. (1861) Chemische Studien Vienna, Austria-Hungary: Carl Gerold's Sohn.
- Chaim Weizmann chemistryexplained.com
- ^ Greiner, Camara; Funada, C (June 2010). "CEH Marketing Research Report: ACETONE". Chemical Economics Handbook. SRI consulting. Retrieved 2 September 2016.(subscription required)
- "Acetone Uses and Market Data". ICIS.com. October 2010. Archived from the original on 2009-05-15. Retrieved 2011-03-21.
- Acetone (US Gulf) Price Report – Chemical pricing information Archived 2013-05-16 at the Wayback Machine. ICIS Pricing, Retrieved on 2012-11-26
- Myers, Richard Leroy (2007). The 100 Most Important Chemical Compounds: A Reference Guide. Greenwood Press. p. 5. ISBN 9780313337581.
- Wittcoff, M.M.; Green, H.A. (2003). Organic chemistry principles and industrial practice (1. ed., 1. reprint. ed.). Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. p. 4. ISBN 3-527-30289-1.
- Lemal, David M. (2004). "Perspective on Fluorocarbon Chemistry". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 69 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1021/jo0302556. PMID 14703372.
- Hine, Jack; Arata, Kazushi (1976). "Keto-Enol Tautomerism. II. The Calorimetrical Determination of the Equilibrium Constants for Keto-Enol Tautomerism for Cyclohexanone and Acetone". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan. 49 (11): 3089–3092. doi:10.1246/bcsj.49.3089.
- Sowa, John R. (2005). Catalysis of organic reactions. Boca Raton: Taylor & Francis. p. 363. ISBN 978-0-8247-2729-1. OCLC 67767141.
- Driessen, W.L.; Groeneveld, W.L. (1969). "Complexes with ligands containing the carbonyl group. Part I: Complexes with acetone of some divalent metals containing tetrachloro-ferrate(III) and -indate(III) anions". Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas. 88 (8): 77977–988. doi:10.1002/recl.19690880811.
- Kilner, C. A.; Halcrow, M. A. (2006). "An unusual example of a linearly coordinated acetone ligand in a six-coordinate iron(II) complex". Acta Crystallographica C. 62 (9): 1107–1109. Bibcode:2006AcCrC..62M.437K. doi:10.1107/S0108270106028903. PMID 16954630.
- Lozano, A.; Yip, B.; Hanson, R.K. (1992). "Acetone: a tracer for concentration measurements in gaseous flows by planar laser-induced fluorescence". Exp. Fluids. 13 (6): 369–376. Bibcode:1992ExFl...13..369L. doi:10.1007/BF00223244. S2CID 121060565.
- Haynes, p. 15.49
- Kargin, V. A.; Kabanov, V. A.; Zubov, V. P.; Papisov, I. M. (1960). "Polymerisation of acetone". Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR. 134 (5): 1098–1099.
- Kawai, Wasaburo (1962). "Polymerization of Acetone". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan. 35 (3): 516A. doi:10.1246/bcsj.35.516a.
- Cataldo, Franco (1996). "Synthesis of ketonic resins from self-polymerization of acetone, 1 Action of protic and Lewis acids on acetone". Die Angewandte Makromolekulare Chemie. 236 (1): 1–19. doi:10.1002/apmc.1996.052360101.
- ^ Karch, Steven B. (1998). Drug abuse handbook. Boca Raton, Fla.: CRC Press. p. 369. ISBN 978-1-4200-4829-2. OCLC 61503700.
- Amann, Anton; Costello, Ben de Lacy; Miekisch, Wolfram; Schubert, Jochen; Buszewski, Bogusław; Pleil, Joachim; Ratcliffe, Norman; Risby, Terence (2014). "The human volatilome: Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in exhaled breath, skin emanations, urine, feces and saliva". Journal of Breath Research. 8 (3): 034001. Bibcode:2014JBR.....8c4001A. doi:10.1088/1752-7155/8/3/034001. PMID 24946087. S2CID 40583110.
- Glew, Robert H (2010). "You Can Get There From Here: Acetone, Anionic Ketones and Even-Carbon Fatty Acids can Provide Substrates for Gluconeogenesis". Nig. J. Physiol. Sci. 25: 2–4. Archived from the original on 2013-09-26. Retrieved 2013-09-01.
- Miller, DN; Bazzano, G (1965). "Propanediol metabolism and its relation to lactic acid metabolism". Ann NY Acad Sci. 119 (3): 957–973. Bibcode:1965NYASA.119..957M. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb47455.x. PMID 4285478. S2CID 37769342.
- Ruddick, JA (1972). "Toxicology, metabolism, and biochemistry of 1,2-propanediol". Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 21 (1): 102–111. Bibcode:1972ToxAP..21..102R. doi:10.1016/0041-008X(72)90032-4. PMID 4553872.
- Wittcoff, Harold; Reuben, B. G.; Plotkin, Jeffrey S. (2004). Industrial organic chemicals. Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley-Interscience. p. 259. ISBN 0-471-44385-9. OCLC 53307689.
- Ivanov, Vitalii; Trojanowska, Justyna; Machado, Jose; Liaposhchenko, Oleksandr; Zajac, Jozef; Pavlenko, Ivan; Edl, Milan; Perakovic, Dragan (2019). Advances in design, simulation and manufacturing II : proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Design, Simulation, Manufacturing: The Innovation Exchange, DSMIE-2019, June 11–14, 2019, Lutsk, Ukraine. Cham. pp. 430–435. ISBN 978-3-030-22365-6. OCLC 1104227601.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) – Safety Hazard Information – Special Hazards of Acetylene Archived 2016-01-22 at the Wayback Machine. Msha.gov. Retrieved on 2012-11-26.
- History – Acetylene dissolved in acetone Archived 2015-09-15 at the Wayback Machine. Aga.com, Retrieved on 2012-11-26
- Weiner, Myra L.; Lois A. Kotkoskie (1999). Excipient Toxicity and Safety. Taylor & Francis. p. 32. ISBN 978-0-8247-8210-8.
- Inactive Ingredient Search for Approved Drug Products, FDA/Center for Drug Evaluation and Research
- "Cleaning Glassware" (PDF). Wesleyan University. September 2009. Retrieved July 7, 2016.
- What is an Azeotrope?. Solvent—recycling.com. Retrieved on 2012-11-26.
- Engbaek, K; Johansen, KS; Jensen, ME (February 1979). "A new technique for Gram staining paraffin-embedded tissue". Journal of Clinical Pathology. 32 (2): 187–90. doi:10.1136/jcp.32.2.187. PMC 1145607. PMID 86548.
- Addison, Ault (1998). Studyguide for Techniques and Experiments for Organic Chemistry. Sausalito, CA. p. 310. ISBN 978-0-935702-76-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Davis, Gretchen; Hall, Mindy (2012). The makeup artist handbook : techniques for film, television, photography, and theatre. Waltham, MA: Focal Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-240-81894-8. OCLC 776632427.
- "Acetone". Chemical Safety Facts. Retrieved 2024-05-27.
- "How to Take Off Gel & Acrylic Nails | Just Ask Sally". www.sallybeauty.com. Retrieved 2024-05-27.
- ^ Simpson, Deborah M.; Beynon, Robert J. (2009-12-14). "Acetone Precipitation of Proteins and the Modification of Peptides". Journal of Proteome Research. 9 (1). American Chemical Society (ACS): 444–450. doi:10.1021/pr900806x. ISSN 1535-3893. PMID 20000691.
- Basten, O.; Bandorski, D.; Bismarck, C.; Neumann, K.; Fisseler-Eckhoff, A. (2009). "Acetonkompression". Der Pathologe (in German). 31 (3): 218–224. doi:10.1007/s00292-009-1256-7. PMID 20012620. S2CID 195684316.
- Leung, C. A. W.; Fazzi, G. E.; Melenhorst, J.; Rennspiess, D.; Grabsch, H. I. (November 2018). "Acetone clearance of mesocolic or mesorectal fat increases lymph node yield and may improve detection of high-risk Stage II colorectal cancer patients" (PDF). Colorectal Disease. 20 (11): 1014–1019. doi:10.1111/codi.14335. PMID 29989291. S2CID 205030844.
- MacFarlane, Deborah F. (2010). Skin cancer management : a practical approach. New York: Springer. p. 35. ISBN 978-0-387-88495-0. OCLC 663098001.
- ^ Likhodii SS; Serbanescu I; Cortez MA; Murphy P; Snead OC; Burnham WM (2003). "Anticonvulsant properties of acetone, a brain ketone elevated by the ketogenic diet". Ann Neurol. 54 (2): 219–226. doi:10.1002/ana.10634. PMID 12891674. S2CID 3213318.
- American Chemistry Council Acetone Panel (September 10, 2003). "Acetone (CAS No. 67-64-1) VCCEP Submission" (PDF). pp. 6, 9. Retrieved 2018-04-14.
- ^ "Acetone MSDS". hazard.com. 1998-04-21. Archived from the original on 2012-07-09. Retrieved 2012-11-26.
- Hauptmanns, Ulrich (2014). Process and plant safety. Berlin. p. 20. ISBN 978-3-642-40954-7. OCLC 888160502.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Haynes, p. 16.3
- Haynes, p. 16.5
- Bingham, Eula; Cohrssen, Barbara; Patty, F. A. (2012). Patty's toxicology. Hoboken, New Jersey. p. 736. ISBN 978-1-62198-026-1. OCLC 810064538.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Basic Information on Acetone. Ccohs.ca (1999-02-19). Retrieved on 2012-11-26.
- ^ "SIDS Initial Assessment Report: Acetone" (PDF). Environmental Protection Agency. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-03-09. Retrieved 2014-09-11.
- "What are the potential health effects of acetone?". Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety. Archived from the original on 2008-10-17. Retrieved 2008-10-21.
- Safety (MSDS) data for propanone Archived 2018-03-16 at the Wayback Machine sciencelab.com/msds Retrieved on 2018-03-19
- ^ Acetone, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry ToxFAQs, 1995
- Darwent, B. deB.; Allard, M. J.; Hartman, M. F.; Lange, L. J. (1960). "The Photolysis of Acetone". Journal of Physical Chemistry. 64 (12): 1847–1850. doi:10.1021/j100841a010.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (June 16, 1995). "Air Quality: Revision to Definition of Volatile Organic Compounds—Exclusion of Acetone" (PDF). Federal Register. 60 (116): 31634–31637.
- Jordans, Frank (30 July 2015). "Philae probe finds evidence that comets can be cosmic labs". The Washington Post. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 23 December 2018. Retrieved 30 July 2015.
- "Science on the Surface of a Comet". European Space Agency. 30 July 2015. Retrieved 30 July 2015.
- Bibring, J.-P.; Taylor, M.G.G.T.; Alexander, C.; Auster, U.; Biele, J.; Finzi, A. Ercoli; Goesmann, F.; Klingehoefer, G.; Kofman, W.; Mottola, S.; Seidenstiker, K.J.; Spohn, T.; Wright, I. (31 July 2015). "Philae's First Days on the Comet – Introduction to Special Issue". Science. 349 (6247): 493. Bibcode:2015Sci...349..493B. doi:10.1126/science.aac5116. PMID 26228139.
Common sources
- Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4987-5429-3.
Further reading
- International Chemical Safety Card 0087
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
- Acetone Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
- Hazardous substances databank entry at the national library of medicine Archived 2018-12-04 at the Wayback Machine
- SIDS Initial Assessment Report for Acetone from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
- Calculation of vapor pressure, liquid density, dynamic liquid viscosity, surface tension of acetone
| Cholesterol and steroid metabolic intermediates | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mevalonate pathway |
| ||||||||||
| Non-mevalonate pathway | |||||||||||
| To Cholesterol | |||||||||||
| From Cholesterol to Steroid hormones |
| ||||||||||
| Nonhuman |
| ||||||||||