| This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources. Find sources: "3C-BZ" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2019) |
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 1-propan-2-amine | |
| Other names 4-Benzyloxy-3,5-methoxyamphetamine | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C18H23NO3 |
| Molar mass | 301.386 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
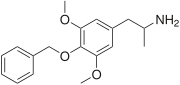
3C-BZ (4-benzyloxy-3,5-dimethoxyamphetamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine. 3C-BZ was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 25–200 mg and the duration as 18–24 hours. According to anecdotal reports from the substance's entry in PiHKAL, 3C-BZ's effects can vary significantly, ranging from intensified emotions and strange dreams, to effects similar to those of LSD or TMA. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of 3C-BZ.
Synthesis
3C-BZ was originally synthesized by Alexander Shulgin starting from 5-methoxyeugenol (4-allyl-2,6-dimethoxyphenol) through a reaction with benzyl chloride to form the benzyloxy derivative of 5-methoxyeugenol. The obtained benzyl derivative was reacted with tetranitromethane to form 1--2-nitro-1-propene, from which 3C-BZ is obtained by reduction of the nitropropene with lithium aluminium hydride.
Another possible synthetic route would be the reaction of benzyl chloride with syringaldehyde to form 3,5-dimethoxy-4-benzyloxybenzaldehyde followed by condensation with nitroethane to form 1--2-nitro-1-propene. The obtained nitropropene can be reduced using lithium aluminium hydride, Red-Al, or an aluminium-mercury amalgam.
References
- ^ Shulgin, Alexander; Shulgin, Ann (September 1991). PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story. Berkeley, California: Transform Press. ISBN 0-9630096-0-5. OCLC 25627628. 3C-BZ Entry in PiHKAL
| Phenethylamines | |
|---|---|
| Phenethylamines |
|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
| Hallucinogens | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Psychedelics (5-HT2A agonists) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dissociatives (NMDAR antagonists) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deliriants (mAChR antagonists) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||