This is an old revision of this page, as edited by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) at 01:46, 17 March 2011 (Updating {{drugbox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid) per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs)). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 01:46, 17 March 2011 by CheMoBot (talk | contribs) (Updating {{drugbox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid) per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs))(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) Pharmaceutical compound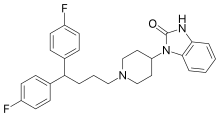 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | oral only |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | at least 40 to 50% |
| Metabolism | hepatic, by cytochrome P450, isoenzymes 3A, and 1A2; metabolites are inactive |
| Elimination half-life | 2 to 3 days (average in one study 55 hours) |
| Excretion | urine, and to a lesser extent in feces |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.520 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C28H29F2N3O |
| Molar mass | 461.56 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Pimozide (Orap) is an antipsychotic drug of the diphenylbutylpiperidine class. It was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1963. It has a high potency compared to chlorpromazine (ratio 50-70:1). On a weight basis it is even more potent than haloperidol. It also has special neurologic indications for Tourette syndrome and resistant tics. The side effects include akathisia, tardive dyskinesia, and, more rarely, neuroleptic malignant syndrome and long QT syndrome.
Uses
Pimozide is used in its oral preparation in schizophrenia and chronic psychosis (on-label indications in Europe only), Tourette syndrome and resistant tics (Europe, USA and Canada). In Germany the 1 mg tablet is indicated for the treatment of some forms of reactive depression.
Off-label use
Pimozide has been used in the treatment of delusional disorder.
It has been used for delusions of parasitosis.
Use as a Listeria monocytogenes inhibitor has been described.
Chemistry
Pimozide is a diphenylbutylpiperidine derivative.
Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics
Plasma levels of pimozide can vary widely between patients, and in insufficient response therapeutic drug monitoring may be required to ascertain that the patient is developing adequate plasma levels before withdrawing the drug and attempting other antipsychotics.
Pharmacodynamics
Pimozide blocks the following postsynaptic receptors according to Bezchlinyk-Butler and Jeffries:
- Extremely strong: D2
- Strong: D3, α1-adrenergic, 5-HT2A
- Moderate: D1, D4, α2-adrenergic
- Weak: mACh, H1
- Extremely weak: 5-HT1A
Pimozide also inhibits moderately the dopamine transporter (DAT), accounting for the stimulant properties of the drug. The inhibition of dopamine-reuptake may also explain the synergistic effects of pimozide in the treatment of ADHD when given together with a stimulant.
Contraindications and precautions
- Contraindicated in patients taking citalopram citalopram(Celexa) and escitalopram escitalopram (Lexapro) due to prolongation of the QTc interval, as per the FDA.
- Patients with prominent agitation or anxiety
- Depressed patients
- Severe intoxication with alcohol, opiates, and psychoactive drugs (e.g. antidepressants, benzodiazepines)
- Preexisting Parkinson's disease
- Comedication with nefazodone, clarithromycin and vetoconazol (see below under interactions)
- Caution: Anticonvulsive treatment in epileptic patients should not be interrupted. Pimozide may in principle lower the seizure-threshold.
- Caution: Patients under 18 yrs. of age. Side effects may be particularly frequent and severe. Treatment should be started with low initial dose and the dose increased very slowly.
Side effects
Further information: Typical antipsychoticPimozide can have severe, potentially fatal side effects. As with other dopamine antagonists pimozide can cause various extrapyramidal side effects, including tardive dyskinesia and Rabbit syndrome. The frequency of extrapyramidal side effects is quite high. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome may also occur.
In particular, pimozide is known for causing the unpleasant extrapyramidal side effect akathisia (commonly referred to as "restless pacing") in a large percentage of those who take it. This "restlessness" can sometimes be treated with anticholinergic drugs (mainly benztropine), beta blockers or benzodiazepines, particularly clonazepam (Klonopin). Unfortunately, in many cases this side effect can be so intense that even large doses of these drugs are unable to counter it, and often is so extreme that self-destructive behaviour, including attempting suicide, may occur.
Pimozide has no significant sedative properties, but behaves in some patients as a mild stimulant. If the drug is given shortly before bedtime, insomnia may result. Excitement, agitation, irritability, tension, anxiety, and nightmares have all been seen.
The drug can also cause depression in quite a number of patients, severe enough to result in suicide.
Pimozide has few but nonetheless existing anticholinerg side effects (e.g. dry mouth, obstipation, urinary hesitancy), rarely of clinical importance.
Pimozide may rarely cause seizures of the grand-mal-type. Patients with epilepsia should be counselled to maintain anticonvulsive therapy.
Particularly disturbing is a relatively high incidence of the long QT syndrome, which may lead to ventricular tachycardia, torsades de pointes and death via ventricular fibrillation.
There is also specific information of carcinogenity both in animals and humans. The carcinogenity in animals has been proven and the carcinogenity in man is strongly suspected (breast cancer and probably liver tumors).
Because of these serious side effects, Pimozide should only be used after the patient has received full information about the drug and agrees to treatment with it despite the risks (fully informed consent).
Given to a non-psychotic patient, Pimozide can result in severe disabilities, both mental and physical. Loss of ability to lead a conversation is a common side effect. Due to that specific side effect, patients who have been wrongly given Pimozide cannot explain their need to stop taking the medication. Pimozide should be prescribed only after a complete medical examination and consensus between the patient and doctor.
There have been reported cases of irreversible nyctalopia in healthy patients treated with Pimozide.
Interactions
- Central Depressants: Action of the other drug may be increased.
- Drugs competing for the same cytochrome subenzymes: Risk of mutual and uncontrollable increased action. Nefazodone, Clarithromycin, Fluconazole and Vetoconazol all lead to increased pimozide plasma levels and to a higher incidence of (potentially serious) side effects of pimozide.
- Grapefruit juice: Elimination of Pimozide is inhibited. Avoid drinking grapefruit juice during treatment with Pimozide.
Dosage
Due to its long halflife pimozide is usually given once a day (preferably in the morning, because pimozide may have a rather stimulating effect).
Recommended dose ranges are as follows:
- Acute psychotic disorders: usually 2 to 12 mg daily starting with low doses, then slowly increasing. More than 20 mg daily should be avoided, because the benefit-risk ratio is unclear
- Chronic psychotic disorders: for maintenance of acute results 6 mg daily is the usual dose
- Tics: 1 to 16 mg daily in slowly increasing doses
- Reactive Depression: 1 to 2 mg daily
- ADHD: not clearly established, start with very small doses (e.g. 0.5 to 1.0 mg) and increase slowly according to the clinical reaction and the side effects encountered.
Animal toxicity and human overdose
The precise lethal dose in humans is unknown. The oral LD50 is 228 mg/kg in mice, 5120 mg/kg in rats, 188 mg/kg in guinea pigs, and 40 mg/kg in dogs.
Generally human overdoses show exaggerations of the pharmacologic effect of Pimozide. These are : ECG-abnormalities, severe extrapyramidal reactions, hypotension, and comatose state with respiratory depression.
Treatment is largely symptomatic. No specific antidote exists. Induction of emesis, gastric lavage and the repeated application of activated charcoal can all be helpful. Monitor and stabilize, if necessary, the vital functions. Hospitialization and/or admittance to intensive care treatment is in most cases necessary. Due to the long halflife of Pimozide, the symptoms of overdose may last for several days.
Synthesis
Janssen, P. A. J.; Soudijn,W.; VanWijngaarden, I.; Dreese A.; Arzneimittel-Forsch. 1968, 18, 282.
- P. Meisel, H.-J. Heidrich, H.-J. Hansch, E. Kretzschman, S. Henker, G. Laban, Ger. (Dem.) DD 243284 (1987).
- P.A.J. Janssen, U.S. patent 3,196,157 (1965).
- P. Janssen, DE 1470124 (1963).
(See also: droperidol)
References
- Munro, A. (1999) Delusional disorder. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-58180-X
- van Vloten WA (2003). "Pimozide: use in dermatology". Dermatol. Online J. 9 (2): 3. PMID 12639456.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Lieberman LA, Higgins DE (2009). "A small-molecule screen identifies the antipsychotic drug pimozide as an inhibitor of Listeria monocytogenes infection". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53 (2): 756–64. doi:10.1128/AAC.00607-08. PMC 2630664. PMID 19015342.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)
External links
| Dopamine receptor modulators | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1-like |
| ||||||
| D2-like |
| ||||||
| Histamine receptor modulators | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 |
| ||||
| H2 |
| ||||
| H3 |
| ||||
| H4 |
| ||||
| Serotonin receptor modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


