
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names PGH2, Endoperoxide H2, Prostaglandin R2 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| MeSH | Prostaglandin+H2 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C20H32O5 |
| Molar mass | 352.465 g/mol |
| Density | 1.129 ± 0.06 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 490 ± 40.0 °C |
| Solubility in water | 0.034 g/L |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Prostaglandin H2 (PGH2), or prostaglandin H2 (PGH2), is a type of prostaglandin and a precursor for many other biologically significant molecules. It is synthesized from arachidonic acid in a reaction catalyzed by a cyclooxygenase enzyme. The conversion from arachidonic acid to prostaglandin H2 is a two-step process. First, COX-1 catalyzes the addition of two free oxygens to form the 1,2-dioxane bridge and a peroxide functional group to form prostaglandin G2 (PGG2). Second, COX-2 reduces the peroxide functional group to a secondary alcohol, forming prostaglandin H2. Other peroxidases like hydroquinone have been observed to reduce PGG2 to PGH2. PGH2 is unstable at room temperature, with a half life of 90–100 seconds, so it is often converted into a different prostaglandin.
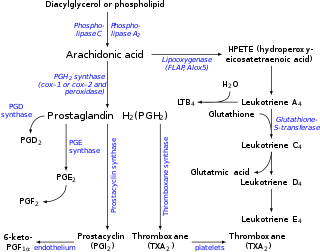
It is acted upon by:
- prostacyclin synthase to create prostacyclin
- thromboxane-A synthase to create thromboxane A2 and 12-(S)-hydroxy-5Z,8E,10E-heptadecatrienoic acid (HHT) (see 12-Hydroxyheptadecatrienoic acid)
- prostaglandin D2 synthase to create prostaglandin D2
- prostaglandin E synthase to create prostaglandin E2
It rearranges non-enzymatically to:
- A mixture of 12-(S)-hydroxy-5Z,8E,10E-heptadecatrienoic acid (HHT) and 12-(S)-hydroxy-5Z,8Z,10E-heptadecatrienoic acid (see 12-hydroxyheptadecatrienoic acid)
Functions of prostaglandin H2:
- regulating the constriction and dilation of blood vessels
- stimulating platelet aggregation
- binds to thromboxane receptor on platelets' cell membranes to trigger platelet migration and adhesion to other platelets.
Effects of aspirin on prostaglandin H2:
- Aspirin has been hypothesized to block the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin

References
- ^ Wishart, David S.; Guo, An Chi; Oler, Eponine; Wang, Fel; Anjum, Afia; Peters, Harrison; Dizon, Raynard; Sayeeda, Zinat; Tian, Siyang; Lee, Brian L.; Berjanskii, Mark; Mah, Robert; Yamamoto, Mai; Jovel Castillo, Juan; Torres Calzada, Claudia; Hiebert Giesbrecht, Mickel; Lui, Vicki W.; Varshavi, Dorna; Varshavi, Dorsa; Allen, Dana; Arndt, David; Khetarpal, Nitya; Sivakumaran, Aadhavya; Harford, Karxena; Sanford, Selena; Yee, Kristen; Cao, Xuan; Budinsky, Zachary; Liigand, Jaanus; Zhang, Lun; Zheng, Jiamin; Mandal, Rupasri; Karu, Naama; Dambrova, Maija; Schiöth, Helgi B.; Gautam, Vasuk. "Showing metabocard for Prostaglandin H2 (HMDB0001381)". Human Metabolome Database, HMDB. 5.0.
- van der Donk WA, Tsai AL, Kulmacz RJ (December 2002). "The cyclooxygenase reaction mechanism". Biochemistry. 41 (52): 15451–8. doi:10.1021/bi026938h. PMID 12501173.
- Salomon RG, Miller DB, Zagorski MG, Coughlin DJ (October 1984). "Prostaglandin endoperoxides. 14. Solvent-induced fragmentation of prostaglandin endoperoxides. New aldehyde products from PGH2 and a novel intramolecular 1,2-hydride shift during endoperoxide fragmentation in aqueous solution". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 106 (20): 6049–6060. doi:10.1021/ja00332a049. ISSN 0002-7863.
- Hla T, Neilson K (August 1992). "Human cyclooxygenase-2 cDNA". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 89 (16): 7384–8. Bibcode:1992PNAS...89.7384H. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.16.7384. PMC 49714. PMID 1380156.
- Woodward DF, Jones RL, Narumiya S (September 2011). "International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXXIII: classification of prostanoid receptors, updating 15 years of progress". Pharmacological Reviews. 63 (3): 471–538. doi:10.1124/pr.110.003517. PMID 21752876.
| Eicosanoids | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precursor | |||||||||||||||
| Prostanoids |
| ||||||||||||||
| Leukotrienes (LT) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Eoxins (EX) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Nonclassic |
| ||||||||||||||
| By function | |||||||||||||||
This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |