This is the current revision of this page, as edited by Graeme Bartlett (talk | contribs) at 05:17, 19 October 2024 (cas). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 05:17, 19 October 2024 by Graeme Bartlett (talk | contribs) (cas)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)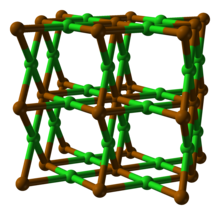
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| PubChem CID | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | PoCl2 |
| Molar mass | 279.91 g/mol |
| Appearance | ruby-red solid |
| Density | 6.50 g cm |
| Melting point | 355 °C (671 °F; 628 K) (sublimes at 130 °C) |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | orthorhombic, oP3 |
| Space group | Pmmm (No 47) |
| Lattice constant | a = 0.367 nm, b = 0.435 nm, c = 0.450 nm |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Polonium dichloride is a chemical compound of the radioactive metalloid, polonium and chlorine. Its chemical formula is PoCl2. It is an ionic salt.
Structure
Polonium dichloride appears to crystallise with an orthorhombic unit cell in either the P222, Pmm2 or Pmmm space group, although this is likely a pseudo-cell. Alternatively, the true space group may be monoclinic or triclinic, with one or more cell angles close to 90°. Assuming the space group is P222, the structure exhibits distorted cubic coordination of Po as {PoCl8} and distorted square planar coordination of Cl as {ClPo4}.
Preparation
PoCl2 can be obtained either by halogenation of polonium metal or by dehalogenation of polonium tetrachloride, PoCl4. Methods for dehalogenating PoCl4 include thermal decomposition at 300 °C, reduction of cold, slightly moist PoCl4 by sulfur dioxide; and heating PoCl4 in a stream of carbon monoxide or hydrogen sulfide at 150 °C.
Reactions
PoCl2 dissolves in dilute hydrochloric acid to give a pink solution, which autoxidises to Po(IV). PoCl2 is rapidly oxidised by hydrogen peroxide or chlorine water. Addition of potassium hydroxide to the pink solution results in a dark brown precipitate – possibly hydrated PoO or Po(OH)2 – which is rapidly oxidised to Po(IV). With dilute nitric acid, PoCl2 forms a dark red solution followed by a flaky white precipitate of unknown composition.
See also
References
- ^ Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils (ed.), Inorganic Chemistry, translated by Eagleson, Mary; Brewer, William, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, p. 594, ISBN 0-12-352651-5
- ^ Bagnall, K. W.; d'Eye, R. W. M.; Freeman, J. H. (1955). "The polonium halides. Part I. Polonium chlorides". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 2320. doi:10.1039/JR9550002320.
| Polonium compounds | |
|---|---|
| Polonium(−II) | |
| Polonium(II) | |
| Polonium(IV) | |
| Polonium(VI) | |

