
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Europium(III) chloride Europium trichloride | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.025 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | EuCl3 |
| Molar mass | 258.323 g/mol 366.41 g/mol (hexahydrate) |
| Melting point | 632 °C (1,170 °F; 905 K) decomposes |
| Solubility in other solvents | Soluble |
| Structure | |
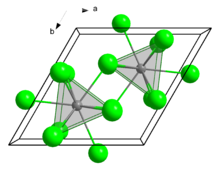
| Crystal structure | hexagonal (UCl3 type), hP8 |
| Space group | P63/m, No. 176 |
| Coordination geometry | Tricapped trigonal prismatic (nine-coordinate) |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Europium(III) oxide |
| Other cations | Samarium(III) chloride Gadolinium(III) chloride |
| Related compounds | Europium dichloride |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Europium(III) chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula EuCl3. The anhydrous compound is a yellow solid. Being hygroscopic it rapidly absorbs water to form a white crystalline hexahydrate, EuCl3·6H2O, which is colourless. The compound is used in research.
Preparation
Treating Eu2O3 with aqueous HCl produces hydrated europium chloride (EuCl3·6H2O). This salt cannot be rendered anhydrous by heating. Instead one obtains an oxychloride. Anhydrous EuCl3 is often prepared by the "ammonium chloride route," starting from either Eu2O3 or hydrated europium chloride (EuCl3·6H2O) by heating carefully to 230 °C. These methods produce (NH4)2:
- 10 NH4Cl + Eu2O3 → 2 (NH4)2 + 6 NH3 + 3 H2O
- EuCl3·6H2O + 2 NH4Cl → (NH4)2 + 6 H2O
The pentachloride decomposes thermally according to the following equation:
- (NH4)2 → 2 NH4Cl + EuCl3
The thermolysis reaction proceeds via the intermediary of (NH4).
Reactions
Europium(III) chloride is a precursor to other europium compounds. It can be converted to the corresponding metal bis(trimethylsilyl)amide via salt metathesis with lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide. The reaction is performed in THF and requires a period at reflux.
- EuCl3 + 3 LiN(SiMe3)2 → Eu(N(SiMe3)2)3 + 3 LiCl
Eu(N(SiMe3)2)3 is a starting material for the more complicated coordination complexes.
Reduction with hydrogen gas with heating gives EuCl2. The latter has been used to prepare organometallic compounds of europium(II), such as bis(pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)europium(II) complexes. Europium(III) chloride can be used as a starting point for the preparation of other europium salts.
Structure
In the solid state, it crystallises in the UCl3 motif. The Eu centres are nine-coordinate.
Bibliography
- Weast, R. C., ed. (1972). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (53rd ed.). Cleveland, Ohio: Chemical Rubber Co.
References
- Meyer, G. (1989). The Ammonium Chloride Route to Anhydrous Rare Earth Chlorides-The Example of YCl3. Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 25. pp. 146–150. doi:10.1002/9780470132562.ch35. ISBN 978-0-470-13256-2.
- Edelmann, F. T.; Poremba, P. (1997). Herrmann, W. A. (ed.). Synthetic Methods of Organometallic and Inorganic Chemistry. Vol. VI. Stuttgart: Georg Thieme Verlag. ISBN 3-13-103021-6.
- Taylor, M.D.; Carter, C.P. (1962). "Preparation of anhydrous lanthanide halides, especially iodides". Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry. 24 (4): 387–391. doi:10.1016/0022-1902(62)80034-7.
- Bradley, Donald C.; Ghotra, Joginder S.; Hart, F. Alan (1973). "Low co-ordination numbers in lanthanide and actinide compounds. Part I. The preparation and characterization of tris{bis(trimethylsilyl)-amido}lanthanides". Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions (10): 1021–1023. doi:10.1039/DT9730001021.
- Tilley, T. Don; Andersen, Richard A.; Spencer, Brock; Ruben, Helena; Zalkin, Allan; Templeton, David H. (1980). "Divalent lanthanide chemistry. Bis (pentamethylcyclopentadienyl) europium(II) and -ytterbium(II) derivatives: crystal structure of bis (pentamethylcyclopentadienyl) (tetrahydrofuran ytterbium(II) -hemitoluene at 176 K". Inorganic Chemistry. 19 (10): 2999. doi:10.1021/ic50212a031.
- Evans, William J.; Hughes, Laura A.; Hanusa, Timothy P. (1986). "Synthesis and x-ray crystal structure of bis(pentamethylcyclopentadienyl) complexes of samarium and europium: (C5Me5)2Sm and (C5Me5)2Eu". Organometallics. 5 (7): 1285. doi:10.1021/om00138a001.
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
| Europium compounds | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Europium(II) | |||
| Europium(III) |
| ||
| Lanthanide salts of halides | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
