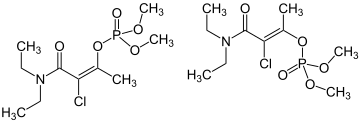
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name (E/Z)- dimethyl phosphate | |
| Other names Dimecron | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.032.818 |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C10H19ClNO5P |
| Molar mass | 299.69 g·mol |
| Density | 1.2132 g/cm |
| Melting point | 120 to 123 °C (248 to 253 °F; 393 to 396 K) |
| Boiling point | 162 °C (324 °F; 435 K) (1.5 mmHg) |
| Solubility in water | Miscible |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) | 13 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 6 mg/kg (mouse, IV) 20 mg/kg (rat, oral) 26 mg/kg (rat, subcut.) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Phosphamidon is an organophosphate insecticide first reported in 1960. It acts as a cholinesterase inhibitor.
The commercial product typically exists as a mixture of 70% (Z)-isomer and 30% (E)-isomer.
Toxicity and regulation
Phosphamidon is very highly toxic to mammals and is listed as WHO Hazard Class Ia. A harvester developed symptoms of moderately severe poisoning after working in a field that had been sprayed with the chemical 2 weeks earlier. He collapsed and exhibited significant depression of serum cholinesterase, but recovered completely within 2 days after successful treatment with atropine. International trade of phosphamidon is covered by the Rotterdam Convention.
References
- ^ Data Sheet on Pesticides No. 74: Phosphamidon, International Programme on Chemical Safety
- ^ Bachmann, Fritz (1960). "Phosphamidon, a new phosphate ester with systemic action". Proc. Intern. Cong. Crop. Protection, 4th Congr., Hamburg. 2: P1153-1155.
- ^ Jacques, R.; Bein, H. J. (1960). "Toxicology and pharmacology of a new systemic phosphoric acid ester insecticide phosphamidon (2-chloro-2-diethylcarbamoyl-1-methylvinyl dimethyl phosphate)". Archiv für Toxikologie. 18: 316–330. doi:10.1007/BF02226232. S2CID 6714997.
- S. Gitelson, J. T. Davidson, A. Werczberger. Phosphamidon poisoning. Br. J. Ind. Med. 22: 236-239, 1965.