| Revision as of 07:09, 30 November 2023 editBoghog (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, IP block exemptions, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers, Template editors137,799 edits consistent citation formatting; templated cites← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 14:19, 18 April 2024 edit undoJJMC89 bot III (talk | contribs)Bots, Administrators3,684,792 editsm Moving Category:Thiosemicarbazone to Category:Thiosemicarbazones per Misplaced Pages:Categories for discussion/Speedy | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:19, 18 April 2024
Chemical compound Pharmaceutical compound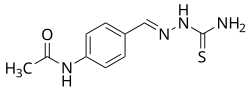 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Conteben |
| Other names | Thiacetazone; Thiocetazone; Thioparamizone; Benzothiozane; 4-Acetylaminobenzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone; N-phenyl]acetamide |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.882 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H12N4OS |
| Molar mass | 236.29 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Thioacetazone (INN, BAN), also known as amithiozone (USAN), is an oral antibiotic which is used in the treatment of tuberculosis. It has fallen into almost complete disuse due to toxicity and the introduction of improved anti-tuberculosis drugs like isoniazid. The drug has only weak activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and is only useful in preventing resistance to more powerful drugs such as isoniazid and rifampicin. It is never used on its own to treat tuberculosis; it is used in a similar way to ethambutol.
There is no advantage to using thioacetazone if the regimen used already contains ethambutol, but many countries in sub-Saharan Africa still use thioacetazone because it is extremely cheap. Use of thioacetazone is declining because it can cause severe (sometimes fatal) skin reactions in HIV positive patients.
The biological target of thioacetazone has proven elusive and its mechanism of action remains unknown, although it is thought to interfere with mycolic acid synthesis.
Adverse effects
One of the documented adverse effects of thioacetazone is the excessive accumulation of serum (or blood plasma) in the brain. Another is weakening of the thyroid glands. These were found in a treatment combining conteben with PAS acid p-amino-salicylic acid.
See also
References
- Buckingham J (2 December 1993). Dictionary of Natural Products. CRC Press. pp. 208–. ISBN 978-0-412-46620-5.
- Martindale: The Extra Pharmacopoeia (30th ed.). London: The Pharmaceutical Press. 1993. p. 217. ISBN 978-0-85369-300-0.
- "List of Antituberculosis agents - Generics Only". Drugs.com.
- ^ Grayson ML, Crowe SM, McCarthy JS, Mills J, Mouton JW, Norrby SR, Paterson DL, Pfaller MA (29 October 2010). "Thioacetazone". Kucers' The Use of Antibiotics: A Clinical Review of Antibacterial, Antifungal and Antiviral Drugs (Sixth ed.). CRC Press. pp. 1673–. ISBN 978-1-4441-4752-0.
- Schaaf HS, Seddon JA, Caminero JA (2011). "Second-line Antituberculosis Drugs: Current Knowledge, Recent Research Findings and Controversies". In Donald PR, Van Helden PD (eds.). Antituberculosis Chemotherapy. Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers. pp. 92–. ISBN 978-3-8055-9627-5.
- Rieder HL, Arnadottir T, Trébucq A, Enarson DA (January 2001). "Tuberculosis treatment: dangerous regimens?". The International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease. 5 (1): 1–3. PMID 11263509.
- Nunn P, Porter J, Winstanley P (1993). "Thiacetazone--avoid like poison or use with care?". Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 87 (5): 578–582. doi:10.1016/0035-9203(93)90096-9. PMID 7505496.
- Bergqvist N, De Mare O (August 1952). "Hypothyroidism and cerebral edema following combined treatment of tuberculosis with conteben (TB I 698) and p-amino-salicylic acid". Acta Medica Scandinavica. 143 (5): 323–335. doi:10.1111/j.0954-6820.1952.tb14267.x. PMID 12976024.
External links
- "Conteben". Chemindustry. Archived from the original on 23 February 2012.
- "Wie einst Robert Koch". Der Spiegel Wissenschaft. 25 December 1951.
Im November 1947 macht der für alles Neue aufgeschlossene Freiburger Internist Professor Dr. Ludwig Heilmeyer, ein Mitschüler des Atomphysikers Heisenberg, die erste schwache Andeutung, daß sich Domagks Präparat in seiner Klinik zu bewähren scheine. Genaue Zahlen gibt aber erst drei Monate später ein bis dahin unbekannter Arzt, Dr. Berthold Mikat, der nur in Vertretung seines Chefs, Dr. Fritz Kuhlmann aus Mölln, spricht: Im Krankenhaus der Landesversicherungsanstalt Schleswig-Holstein ist nach Tb I-Behandlung bei 49 von 66 Patienten mit Lungentuberkulose eindeutige Besserung nachgewiesen worden. Das ist der Start für die Einführung des Tb I, das später den Namen Conteben bekommt.