This is an old revision of this page, as edited by ChemNerd (talk | contribs) at 13:06, 18 December 2010 (removed Category:Phenols using HotCat). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 13:06, 18 December 2010 by ChemNerd (talk | contribs) (removed Category:Phenols using HotCat)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)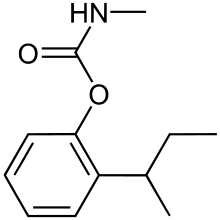
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name (2-Butan-2-ylphenyl) N-methylcarbamate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.021.081 |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C12H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 207.273 g·mol |
| Appearance | Pale yellow or pale red liquid |
| Solubility in water | insoluble |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Fenobucarb is a carbamate insecticide. A pale yellow or pale red liquid, insoluble in water; used as an agricultural insecticide on rice and cotton and highly toxic for humans.
Synonyms
2-(1-methylpropyl)phenol methylcarbamate; 2-(1-methylpropyl)phenyl methylcarbamate; 2-sec-Butylphenyl N-methylcarbamate; BPMC; fenocarb; N-methyl O-sec-butylPhenyl carbamate
Tradenames
Fenobucarb, Osbac, Bassa
LD50
- Male Mouse 340 mg/kg
- Male Rat 410 mg/kg
References
- Takahashi, HIROAKI (1984). "Potentiated Toxicity of 2-sec-Butylphenyl Methylcarbamate (BPMC)". Toxocological Sciences. 4 (5): 718–723. doi:10.1093/toxsci/4.5.718.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - Oregon State University, toxicology sheet
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |