This is the current revision of this page, as edited by OndraMix (talk | contribs) at 08:59, 22 January 2024 (typo). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 08:59, 22 January 2024 by OndraMix (talk | contribs) (typo)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)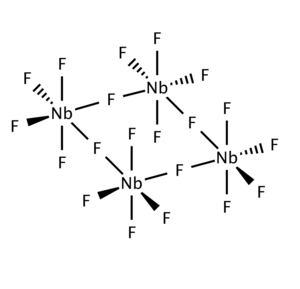
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Niobium(V) fluoride Niobium pentafluoride | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.109 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | F5Nb |
| Molar mass | 187.89839 g·mol |
| Appearance | colorless hygroscopic solid |
| Density | 3.293 g/cm |
| Melting point | 72 to 73 °C (162 to 163 °F; 345 to 346 K) |
| Boiling point | 236 °C (457 °F; 509 K) |
| Solubility in water | reacts |
| Solubility | slightly soluble in chloroform, carbon disulfide, sulfuric acid |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302, H312, H314, H332 |
| Precautionary statements | P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P322, P330, P363, P405, P501 |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Niobium(V) chloride Niobium(V) bromide Niobium(V) iodide |
| Other cations | Vanadium(V) fluoride Tantalum(V) fluoride |
| Related niobium fluorides | Niobium(III) fluoride Niobium(IV) fluoride |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Niobium(V) fluoride, also known as niobium pentafluoride, is the inorganic compound with the formula NbF5. It is a colorless solid.
Preparation and structure
Niobium pentafluoride is obtained by treatment of any niobium compound with fluorine:
- 2 Nb + 5 F2 → 2 NbF5
- 2 NbCl5 + 5 F2 → 2 NbF5 + 5 Cl2
As shown by X-ray crystallography, the solid consists of tetramers 4. This structure is related to that for WOF4.
Reactions
It reacts with hydrogen fluoride to give H2NbF7, a superacid. In hydrofluoric acid, NbF5 converts to and . The relative solubility of K2[MFO] (M = Nb, Ta) is the basis of the Marignac process for separation of Nb and Ta.
NbCl5 forms a dimeric structure (edge-shared bioctahedron) in contrast to the corner-shared tetrameric structure of the fluoride.
External links
References
- Joachim Eckert; Hermann C. Starck (2005). "Niobium and Niobium Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_251. ISBN 3527306730.
- Homer F. Priest (1950). "Anhydrous Metal Fluorides". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 3. p. 171. doi:10.1002/9780470132340.ch47.
- Edwards, A. J. (1964). "717. The structures of niobium and tantalum pentafluorides". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 3714. doi:10.1039/jr9640003714.
| Niobium compounds | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Niobium(II) | |||
| Niobium(III) | |||
| Niobium(IV) | |||
| Niobium(V) |
| ||