| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Selenium tetrachloride | |
| Other names Selenium(IV) chloride, tetrachloro-λ-selane | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.036 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | SeCl4 |
| Molar mass | 220.771 g/mol |
| Appearance | white to yellow crystals |
| Density | 2.6 g/cm, solid |
| Melting point | sublimes at 191.4 °C |
| Solubility in water | decomposes in water |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | Monoclinic, mS80 |
| Space group | C12/c1, No. 15 |
| Molecular shape | Seesaw (gas phase) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |   
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H301, H331, H373, H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P301+P310, P304+P340, P311, P314, P321, P330, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Flash point | non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Selenium tetrafluoride Selenium tetrabromide Selenium dioxide |
| Other cations | Dichlorine monoxide Sulfur tetrachloride Tellurium tetrachloride |
| Related compounds | Selenium dichloride |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Selenium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound composed with the formula SeCl4. This compound exists as yellow to white volatile solid. It is one of two commonly available selenium chlorides, the other example being selenium monochloride, Se2Cl2. SeCl4 is used in the synthesis of other selenium compounds.
Synthesis and structure

The compound is prepared by treating selenium with chlorine. When the reacting selenium is heated, the product sublimes from the reaction flask. The volatility of selenium tetrachloride can be exploited to purification of selenium.
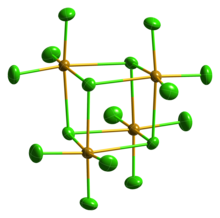
Solid SeCl4 is actually a tetrameric cubane-type cluster, for which the Se atom of an SeCl6 octahedron sits on four corners of the cube and the bridging Cl atoms sit on the other four corners. The bridging Se-Cl distances are longer than the terminal Se-Cl distances, but all Cl-Se-Cl angles are approximately 90°.
SeCl4 has often been used as an example for teaching VSEPR rules of hypervalent molecules. As such, one would predict four bonds but five electron groups giving rise to a seesaw geometry. This clearly is not the case in the crystal structure. Others have suggested that the crystal structure can be represented as SeCl3 and Cl. This formulation would predict a pyramidal geometry for the SeCl3 cation with a Cl-Se-Cl bond angle of approximately 109°. However, this molecule is an excellent example of a situation where maximal bonding cannot be achieved with the simplest molecular formula. The formation of the tetramer (SeCl4)4, with delocalized sigma bonding of the bridging chloride is clearly preferred over a "hypervalent" small molecule. Gaseous SeCl4 contains SeCl2 and chlorine, which recombine upon condensation.
Reactions
Selenium tetrachloride can be reduced in situ to the dichloride using triphenylstibine:
- SeCl4 + SbPh3 → SeCl2 + Cl2SbPh3
Selenium tetrachloride reacts with water to give selenous and hydrochloric acids:
- SeCl4 + 3 H2O → H2SeO3 + 4 HCl
Upon treatment with selenium dioxide, it gives selenium oxychloride:
- SeCl4 + SeO2 → 2SeOCl2
References
- Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. p. 487. ISBN 0-8493-0594-2. Retrieved 2008-07-02.
- "323527 Selenium tetrachloride". Sigma-Aldrich. Retrieved 2008-07-02.
- Nowak, H. G.; Suttle, J. F.; Parker, W. E.; Kleinberg, J. (1957). "Selenium (IV) Chloride". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 5. p. 125. doi:10.1002/9780470132364.ch33. ISBN 9780470132364.
- Kristallstruktur der stabilen Modifikation von SeCl4, Zeitschrift für Naturforschung, 36b, 1660, 1981
- Wells, Structural Inorganic Chemistry, fifth ed, Oxford, p. 709, ISBN 0-19-855370-6
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
| Selenium compounds | |
|---|---|
| Se(−II) | |
| Se(0,I) | |
| Se(I) | |
| Se(II) | |
| Se(IV) | |
| Se(VI) | |
| Se(IV,VI) | |
| Prostanoid signaling modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||